What is cloud security?
Cloud security refers to the practices, technologies, policies, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure within cloud computing environments. Successful cloud security protects sensitive information, ensures compliance with regulatory standards, and mitigates cyber risks. It’s not just about defense; it’s about enabling organizations to harness the full potential of the cloud with confidence and resilience.
Why Is Cloud Security Important?
The shift to cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including scalability, cost savings, and global accessibility. However, it also introduces new security challenges:
- Data Breaches: Misconfigurations and unauthorized access can lead to significant data exposures.
- Compliance Risks: Failing to meet regulatory requirements can result in legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Complex Environments: Managing security across hybrid and multi-cloud environments increases complexity.
According to Gartner, by 2025, 99% of cloud security failures will be the customer’s fault, emphasizing the need for organizations to take proactive security measures.
How Does Cloud Security Work?
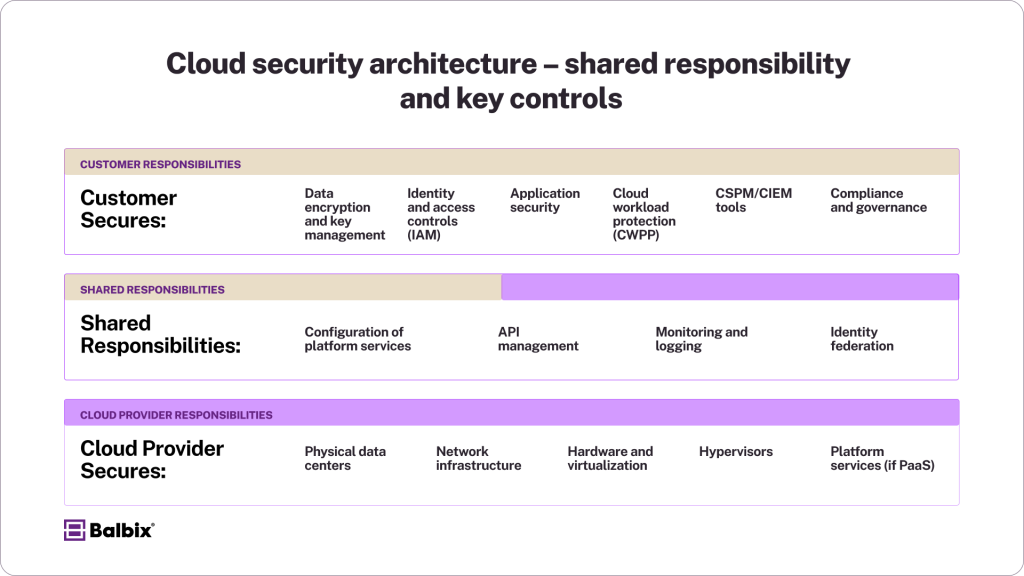
Cloud security operates on a shared responsibility model, where cloud providers secure the infrastructure, and customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and access controls. Key components include:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources.
- Encryption: Protects data at rest and in transit from unauthorized access.
- Security Monitoring: Continuously monitors for threats and vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Management: Ensures adherence to industry and regulatory standards.
Key Aspects of Cloud Security
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implementing strong IAM policies is crucial. This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and the principle of zero trust and least privilege to minimize unauthorized access risks.
2. Data Protection
Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. Utilize key management services to control access to encryption keys. Regularly back up data to prevent loss from accidental deletion or ransomware attacks.
3. Network Security
Segment networks to isolate critical resources. Use firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems to monitor and control traffic. Implement Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) for secure communication.
4. Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Deploy Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to collect and analyze security logs. Establish an incident response plan to address and mitigate security incidents quickly.
5. Compliance and Governance
Adhere to frameworks like the Cloud Security Alliance’s Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) to ensure comprehensive security coverage and regulatory compliance.
Cloud Security Controls
Cloud security controls are measures implemented to protect cloud environments. They can be categorized as:
- Preventive Controls: Aim to prevent security incidents (e.g., firewalls, encryption).
- Detective Controls: Identify and detect security incidents (e.g., intrusion detection systems).
- Corrective Controls: Address and fix security incidents (e.g., patch management).
- Deterrent Controls: Discourage malicious activities (e.g., security policies).
Cloud Security Best Practices
To effectively secure cloud environments, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
- Understand the Shared Responsibility Model: Clearly define security responsibilities between the cloud provider and your organization.
- Implement Strong IAM Policies: Use MFA, RBAC, and enforce the principle of least privilege.
- Encrypt Data: Ensure data is encrypted at rest and in transit.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keep all systems and applications up to date to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Assess and improve security measures continuously.
- Monitor and Log Activities: Implement logging and monitoring to detect and respond to threats promptly.
- Train Employees: Educate staff on security policies and best practices to prevent human errors.
How Balbix Enhances Cloud Security
Balbix provides a comprehensive platform that combines Cyber Asset Attack Surface Management (CAASM) with Risk-Based Exposure Management and Cyber Risk Quantification (CRQ). This enables organizations to:
- Gain Visibility: Understand the complete inventory of cloud assets and their security posture.
- Prioritize Risks: Identify and address the most critical vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
- Quantify Risk: Assess potential breach impacts in monetary terms to inform decision-making.
Conclusion
Cloud security is a critical component of modern IT infrastructure. By understanding its key aspects, implementing robust controls, and following best practices, organizations can protect their cloud environments against evolving threats. Solutions like Balbix further empower organizations to manage and mitigate risks effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is cloud security?
-
Cloud security refers to the technologies, policies, and strategies that protect cloud environments, including data, applications, and infrastructure, from cyber threats. It ensures sensitive information remains secure, helps meet compliance regulations, and mitigates risks for businesses relying on cloud computing.
- Why Is Cloud Security Critical for Businesses?
-
Cloud security is essential because it safeguards data against breaches, ensures compliance with legal frameworks, and reduces the risk of costly downtime. As more businesses adopt cloud platforms, secure environments are key to maintaining trust and operational resilience.
- What Are the Key Components of Cloud Security?
-
Effective cloud security includes several components, such as:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user access through policies like multi-factor authentication.
- Data Encryption: Protects information during storage and transmission.
- Security Monitoring: Continuously detects and mitigates threats.
- Compliance Management: Ensures adherence to industry standards, such as SOC 2 or GDPR.
- What Are Some Best Practices for Strengthening Cloud Security?
-
To enhance cloud security:
- Implement strong IAM policies with principles like zero trust.
- Encrypt all data, both in storage (at rest) and during transfer (in transit).
- Regularly patch and update systems to close vulnerabilities.
- Monitor all activities and assets continuously.
- Provide employee training to prevent human errors.
- How Does the Shared Responsibility Model Impact Cloud Security?
-
The shared responsibility model divides security roles between the cloud provider and the organization:
- Cloud Provider: Handles physical security and secures core infrastructure.
- Organization: Protects data, applications, and user access within the cloud.
Understanding this division helps businesses effectively implement their security strategies.