What is cloud computing?
Popular cloud vendor Amazon Web Services describes cloud computing as follows: cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, cloud computing allows you to access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), there are five essential characteristics to the cloud computing model: on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity and measured service.
Cloud computing has fundamentally changed how we access computing resources. Nicholas Carr explains the shift in his book, The Big Switch: Rewiring the World, from Edison to Google, by comparing changes in the production of electricity and cloud computing.
Nicholas argues that just as the turn of the last century brought a huge shift in electricity production, with cloud computing, now we’re on the verge of a sea change in the way we use computers. Electricity went from being something that individual factories generated for their use, to a centralized utility that powered whole cities. Now, the advent of cloud computing has moved computing from something that traditionally happened only on the hard drive of your computer, to something that happens remotely on the server farms. As the world moved from owning the electricity infrastructure to the centralized grids, people started paying for electricity on a per-use basis. Cloud computing caused a similar shift while embracing pay-as-you-use philosophy for the compute resources.
Cloud computing offers many benefits to the organizations. It gives an unprecedented ability to be more agile, embrace speed, and innovate at scale. The shift to cloud computing has revolutionized how we work, collaborate and communicate.
Types of cloud environments
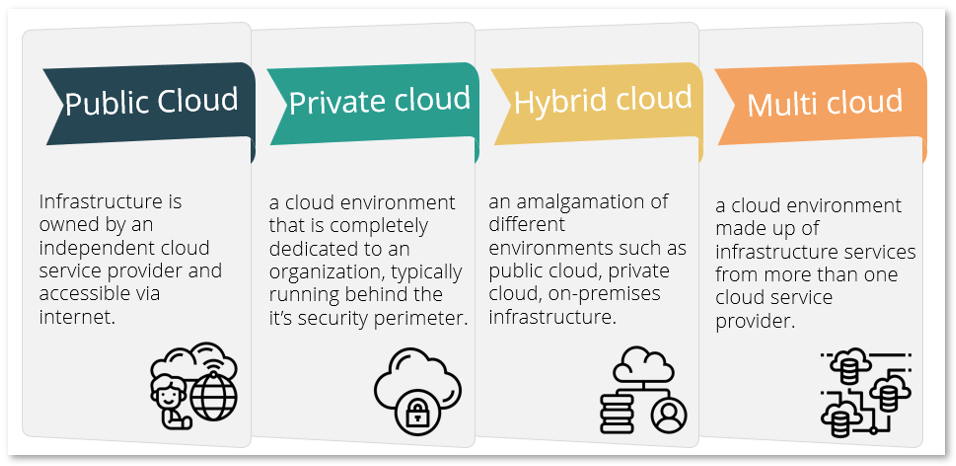
There are four main types of cloud computing environments. These are: public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud and multi cloud. Each can be described as follows:
1. Public clouds:
Public cloud is a cloud environment where the infrastructure is owned by an independent cloud service provider and accessible via the internet. Think of the public cloud as a massive collection of instantly accessible computing resources, including networking, memory, CPU, and storage. You can access these resources on a ‘pay-as-you-use’ basis.
Public clouds are hosted by public cloud vendors on their globally dispersed data centers. Some of the most prominent cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Public cloud use case:
Assume you run a business wherein c infrastructure demand goes up during certain times of the year. As an example, a website covering soccer news will experience a high demand for computing resources during annual soccer championships. You can procure additional capacity for the infrastructure in-house but that would mean your servers are under-utilized for most of the year. Instead, choosing to use a public cloud will give you an option to expand your infrastructure during the peak season and just pay for your usage without incurring the cost of ownership. It will significantly reduce your operational costs.
2. Private clouds:
A private cloud is a cloud environment that is completely dedicated to an organization, typically running within its security perimeter. One can think of private cloud as quite the opposite to the public cloud as the infrastructure is housed within the enterprise, using its own hardware and tools.
Private cloud use case:
Regulatory compliance is one of the use cases for private cloud adoption. For instance, local laws in some countries require their citizens’ data to reside in locally hosted data centers. There are other reasons an organization could potentially adopt a private cloud to meet their specific business requirements, for example, low latency.
3. Hybrid clouds:
A hybrid cloud represents an amalgamation of different environments such as public cloud, private cloud and on-premise infrastructure. Organizations that deploy a hybrid cloud usually invest in tooling to be able to seamlessly orchestrate their operations across all the supported environments. A hybrid cloud allows an organization to pick the appropriate computing environment for each task.
Hybrid cloud use case:
Hybrid clouds have the flexibility to handle and shift computing loads to accommodate changes in demand. For example, if the on-premise compute capacity to run an application is exhausted, a typical hybrid cloud environment will use on-demand cloud resources to provide supplemental compute capacity and thereby ensure high availability and optimal performance.
Hybrid cloud environments are also helpful to effectively manage disaster recovery scenarios. Organizations normally tend to mirror the mission-critical private infrastructure to an equivalent cloud deployment. If onsite services are disrupted, then hybrid cloud setup allows operations to seamlessly move to a cloud instance without causing disruption.
4. Multi cloud:
A multi cloud environment is a cloud environment made up of infrastructure services from more than one cloud service provider. A multi cloud approach is increasingly common for enterprises that want to improve security, performance, achieve agility, flexibility and more.
Multi cloud use case:
A key benefit of a multi cloud approach is that it can help avoid risks specific to vendor lock-in. Multi cloud approach also provides flexibility more generally, for example having a multi cloud setup for business critical scenarios ensures that organizations have the flexibility to switch anytime to ensure service availability.
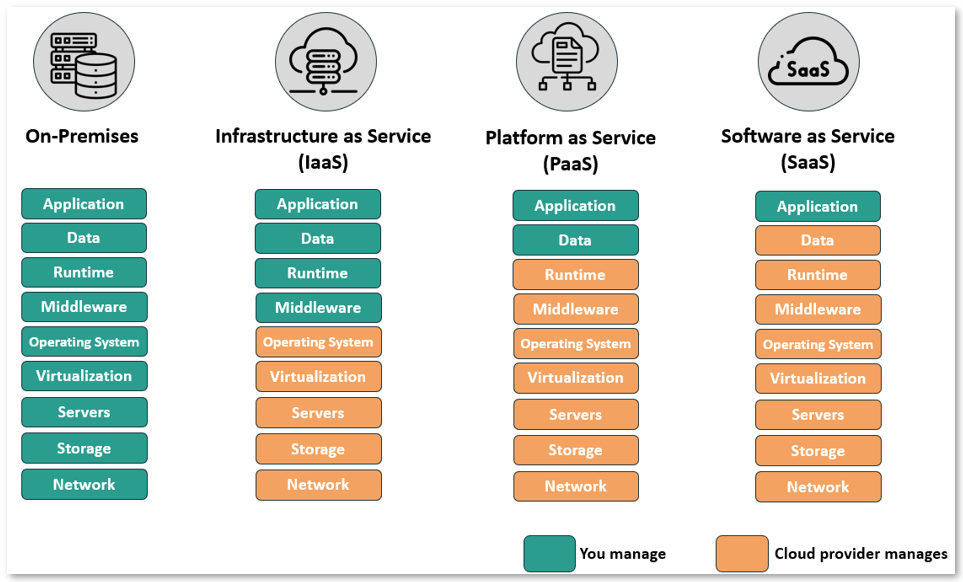
Types of cloud computing models:
The common purpose of the cloud environments described above is for the provision of computing infrastructure. However, there are three fundamental models of cloud computing: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS). They can be described as follows:
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS):
IaaS is a cloud computing model that enables the building blocks of computing – virtual machines, compute, storage, network, servers and more – to be delivered as a service over the internet. An example of IaaS is Google Cloud Compute Engine. Compute Engine is a computing and hosting service that lets you create and run virtual machines on Google infrastructure. Without any upfront capital investments, Compute Engine allows you to run thousands of virtual CPUs on a system that offers quick, consistent performance.
Platform as a service (PaaS):
PaaS is a cloud computing model that allows you to provision, instantiate, run and manage a bundle that includes a computing platform (virtual servers, storage, networking) and tools/software needed by developers to build, manage the applications. You can think of PaaS as a cloud service model that provides you with a configurable application platform including a pre-installed software stack. Azure App Service is one example of a fully managed PaaS. It is an HTTP-based service for hosting web applications, REST APIs, and mobile back ends. It allows developers to build using the language of their choice and run the applications at scale with ease.
Software as a service (SaaS):
SaaS is a cloud computing model in which software is centrally hosted and is licensed on a subscription basis. You can think of SaaS as a cloud services delivery model that offers an on-demand online software subscription. This is one of the most popular cloud computing models. Instead of installing and maintaining software, the SaaS model allows you to access the application via the internet, and not worry about software and hardware management. Google’s suite of applications, Zoom’s video conferencing, Salesforce CRM, Altassian Jira are the popular examples of SaaS applications.