What is the average cost of a data breach in 2024? It’s an eye-watering $4.88M, which means businesses can no longer rely on traditional cybersecurity alone. Organizations must adopt a new approach to stay competitive and operational in an increasingly hostile digital environment. Enter cyber resilience.
Cyber resilience goes beyond prevention, equipping organizations with the tools to effectively detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. This guide will explain cyber resilience, why it matters, its key components, and how to build a cyber-resilient organization.
What is Cyber Resilience?
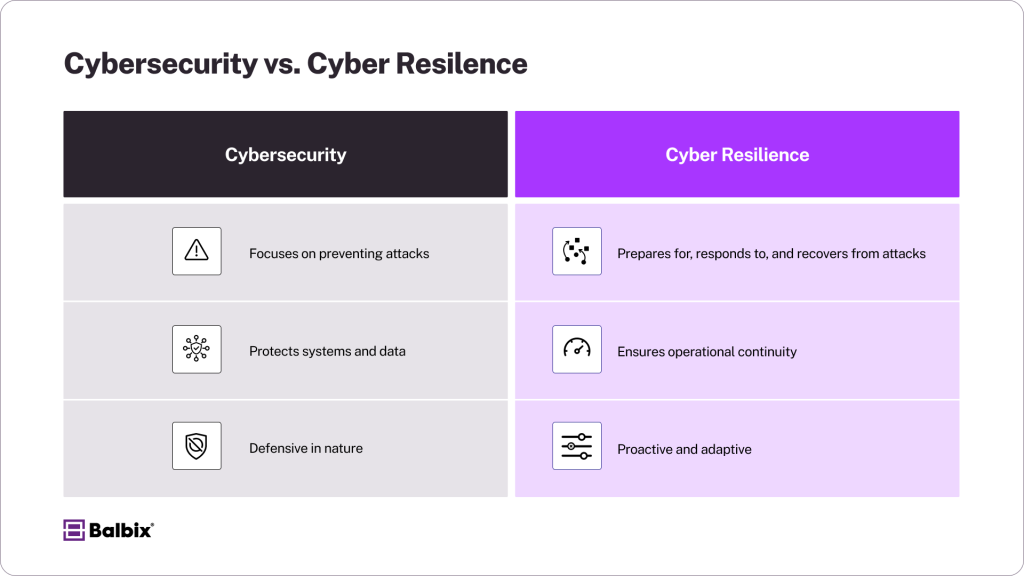
Cyber resilience is an organization’s ability to withstand, recover from, and adapt to cyber threats while maintaining business operations. Unlike traditional cybersecurity, which focuses primarily on protection and defense, cyber resilience ensures businesses can quickly bounce back from attacks, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
Why is Cyber Resilience Important?
Cyberattacks are no longer a question of “if” but “when.” Organizations across industries are increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats due to remote work, cloud technologies, and more sophisticated attackers.
Here’s why cyber resilience is critical in a modern business context:
- Inevitability of Attacks: Cyber threats are becoming more advanced and frequent. Even with the best defenses, no system is 100% secure.
- Financial Impact: Recovery costs—from paying ransomware demands to operational downtime—are skyrocketing. Resilience helps reduce these costs.
- Reputation Management: A quick recovery post-breach minimizes damage to your brand and maintains customer trust.
- Regulatory Compliance: Regulations like GDPR and CCPA demand organizations maintain solid data protection measures. Cyber resilience ensures compliance while avoiding hefty fines.
- Expansion of Attack Surfaces: With remote work and increasing reliance on cloud services, the potential entry points for attackers continue to grow amongst an attack surface.
Cyber Resilience in Action
Picture this: a global retail company faces a ransomware attack that encrypts its key operational data. A company with strong cybersecurity measures might prevent this from happening, but if the attack succeeds, can it recover quickly?
With a detailed cyber resilience strategy, it would already have data backups, incident response & disaster recovery plans, and business continuity systems in place to get back on track within hours—not weeks.
Cybersecurity vs. Cyber Resilience
It’s easy to confuse the two, but they serve different purposes. Cyber resilience isn’t just about defense; it’s also about recovery and adaptability.
Key Components of Cyber Resilience
1. Cybersecurity Foundations
Cybersecurity is the backbone of any cyber resilience strategy. It includes various tools and practices to protect your systems from potential threats. These include firewalls to block unauthorized access, endpoint protection to secure devices, encryption to protect sensitive data, and intrusion detection systems to monitor and respond to suspicious activities.
2. Risk Management
Risk management is a continuous process that involves regularly identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities within your systems. This includes scanning for potential threats, patching known software weaknesses promptly, and implementing stronger access controls such as multi-factor authentication. For example, conducting penetration testing can reveal potential entry points for attackers, allowing you to strengthen defenses in advance.
3. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business continuity and disaster recovery planning are critical to ensuring your organization can withstand and quickly recover from unexpected incidents. Develop disaster recovery protocols that outline specific steps during a breach or outage. Implement redundancy systems, such as backup servers, to prevent data loss and maintain operations. Communication strategies are equally important—ensure all stakeholders are informed and prepared.
Define Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) to set clear timelines for restoring services. For instance, how quickly can your e-commerce platform return online after a DDoS attack? The faster the recovery, the less impact the incident will have on revenue and customer trust.
4. Employee Training
Human error remains one of the leading causes of data breaches, making employee training a critical component of your cybersecurity strategy. Regularly educate your team on recognizing phishing attempts, creating strong passwords, and avoiding risky behaviors like clicking on suspicious links.
Additionally, provide hands-on simulations to help staff identify and respond to threats in real-world scenarios. A well-trained workforce acts as an additional layer of defense, significantly reducing the likelihood of successful attacks.
5. Advanced Monitoring and Automation
Advanced monitoring and automation tools are essential for maintaining real-time visibility across your organization’s IT environment. Monitoring platforms equipped with AI capabilities can analyze vast amounts of data, detect unusual patterns, and flag vulnerabilities more efficiently than manual processes. These tools can also automate routine tasks like patch management and threat response, allowing your team to focus on more strategic initiatives.
For example, automated systems can isolate compromised endpoints immediately to prevent further damage, ensuring faster and more effective incident containment.
Benefits of Cyber Resilience
Building cyber resilience isn’t just about defending against threats—it’s about ensuring your business can withstand and recover from them. Here are five key benefits of a strong cyber resilience strategy:
- Minimized Downtime: Ensure your business operations continue to run smoothly, even in the face of a cyberattack. With proper preparation and robust security measures, you can minimize disruptions, avoid costly interruptions, and maintain productivity during critical moments.
- Cost Reduction: Being proactive about cybersecurity helps reduce expenses associated with recovering from attacks, such as data restoration, legal fines, and reputational damage. Preparedness means spending less on fixing problems and more on pushing your business forward.
- Customer Trust: A resilient organization demonstrates to customers that their data is safe and secure. This boosts confidence in your brand and fosters long-term loyalty, as customers are more likely to trust businesses that prioritize their privacy and security.
- Improved Risk Management: By proactively addressing vulnerabilities in your systems, you can significantly reduce potential risks before they become major issues. A strong risk management approach allows your organization to identify threats early and implement strategies to mitigate them effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting data security and privacy regulations protects your business from hefty penalties and legal complications. Staying compliant safeguards your reputation and positions you as a responsible and trustworthy organization in the eyes of regulators and customers.
How to Achieve Cyber Resilience
Building cyber resilience requires a proactive approach that aligns with industry best practices, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). By following its core functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—you can create a robust defense against evolving threats. Here’s how to implement these principles effectively:
- Gain Real-Time Visibility (Identify)
Continuously monitor your entire attack surface to detect vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. Implement asset discovery tools, risk-based visibility solutions, and threat intelligence platforms to maintain a comprehensive view of your digital ecosystem. - Strengthen Identity and Cyber Hygiene (Protect)
Secure access to critical systems with multi-factor authentication (MFA) and robust identity and access management (IAM) controls. Regularly update software, enforce strong credential policies, and automate patch management to eliminate common security gaps. - Prioritize Core Systems Security (Detect & Protect)
Focus on risk-based vulnerability management to safeguard mission-critical systems. AI-driven threat detection, continuous monitoring, and endpoint protection solutions help detect and neutralize threats before they cause damage. - Adopt Network Segmentation (Protect)
Divide networks into isolated security zones to limit an attacker’s lateral movement in case of a breach. For example, HR systems can be segmented from financial databases to prevent unauthorized department access. Implement zero-trust principles to restrict access to only those who genuinely need it. - Enhance Threat Detection & Response (Detect & Respond)
Use AI-powered security tools to analyze behavioral patterns, detect anomalies, and automate risk assessments in real-time. Deploy extended detection and response (XDR) solutions to rapidly identify, contain, and mitigate threats. - Develop a Resilient Recovery Plan (Recover)
A well-defined incident response and recovery plan ensures your organization can bounce back quickly after an attack. Regularly test your backup and disaster recovery processes, and conduct cyber resilience drills to prepare your team for real-world threats.
Read our complete cybersecurity incident response guide.
By aligning with the NIST CSF, organizations can take a structured approach to cyber resilience—reducing risk, strengthening defenses, and ensuring rapid recovery when threats arise.
Why Cyber Resilience is a Business Imperative
Cyber resilience is no longer optional. Organizations that fail to adapt risk severe financial and reputational damage. By incorporating proactive strategies, leveraging real-time monitoring, and focusing on recovery solutions, businesses can maintain continuity, stay compliant, and build trust in an unpredictable digital world.
Are you ready to make cyber resilience a central part of your strategy? Start today by exploring risk visibility tools like Balbix that can help you anticipate threats and adapt faster than your adversaries.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is cyber resilience, and how does it differ from cybersecurity?
-
Cyber resilience is an organization’s ability to withstand, adapt to, and recover from cyber threats while maintaining business operations. Unlike traditional cybersecurity, which focuses on preventing and defending against attacks, cyber resilience ensures businesses can quickly bounce back after a breach, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
- Why is cyber resilience important for businesses in 2025?
-
Cyber resilience is critical as cyber threats become more sophisticated and frequent. With the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.88M in 2024, organizations must go beyond prevention. Cyber resilience helps businesses reduce financial losses, maintain customer trust, ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and sustain operations even during cyber incidents.
- What are the key components of a strong cyber resilience strategy?
-
A robust cyber resilience strategy includes:
-
Cybersecurity foundations: Firewalls, encryption, endpoint protection, and intrusion detection.
-
Risk management: Regular vulnerability assessments, patching, and access controls.
-
Business continuity and disaster recovery: Backup systems and incident response plans.
-
Employee training: Educating staff on phishing, strong passwords, and threat awareness.
-
Advanced monitoring and automation: AI-driven threat detection, real-time visibility, and automated responses.
-
- How can businesses improve their cyber resilience?
-
Businesses can strengthen cyber resilience by:
-
Gaining real-time visibility into risks and vulnerabilities.
-
Implementing multi-factor authentication and strict access controls.
-
Using AI-driven threat detection and response tools.
-
Segmenting networks to limit attack spread.
-
Developing and testing an incident response and recovery plan.
-
- How does cyber resilience support regulatory compliance?
-
Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific cybersecurity standards require organizations to protect sensitive data and maintain breach response plans. Cyber resilience ensures compliance by integrating proactive security measures, real-time risk monitoring, and structured recovery strategies, helping businesses avoid fines and reputational damage.


