Risk-based vulnerability management is a modern cybersecurity approach that prioritizes vulnerabilities based on their potential risk to an organization’s assets.
Unlike traditional methods that treat all vulnerabilities equally, Risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) leverages risk assessment techniques to focus on vulnerabilities that pose the most significant threats. This shift in strategy ensures security teams can allocate their resources efficiently, addressing the most critical risks first.
What is the Difference Between Risk-Based and Traditional Vulnerability Management?
Traditional vulnerability management involves identifying vulnerabilities across systems and addressing them without necessarily understanding the level of risk each one poses. This approach can overwhelm security teams and neglect high-risk vulnerabilities as resources are spread too thin.
Risk-based vulnerability management differs by incorporating contextual factors, such as:
- Threat intelligence: Insights into current cyberattack trends and tactics.
- Asset criticality: The importance of the asset to business operations.
- Exploitability: The likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited by attackers.
By considering these factors, RBVM enables security teams to focus on vulnerabilities that could most harm the organization, improving efficiency and reducing overall risk.
Key Differences at a Glance:
- Traditional management addresses all vulnerabilities.
- RBVM prioritizes vulnerabilities based on risk.
- RBVM reduces wasted effort on low-risk issues.
Benefits of Risk-Based Vulnerability Management
Risk-based vulnerability management brings several advantages that help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture and operational efficiency. Here are the top benefits:
- Focus on Critical Risks: RBVM empowers security teams to focus on vulnerabilities that matter most. By evaluating risk, teams avoid the “patch everything” mindset and address vulnerabilities that pose genuine threats.
- Quicker Response Times: Since RBVM highlights the most critical vulnerabilities, response times are faster. Teams can immediately act on the vulnerabilities that require urgent attention rather than sifting through a long list of non-critical issues.
- Improved Visibility: With RBVM, organizations gain greater visibility into their risk landscape. By understanding the most dangerous vulnerabilities, teams can plan more effectively and ensure the security of the business’s most vital assets.
- Operational Efficiency: Risk-based approaches optimize resource allocation. Instead of dedicating time and energy to less critical issues, teams can focus on the vulnerabilities that significantly impact the organization’s risk posture.
How RBVM Tools Work
Risk-based vulnerability management tools are designed to streamline identifying, assessing, and prioritizing vulnerabilities. Here’s how they work:
- Data Collection: RBVM tools aggregate data from various sources such as security scanners, asset management systems, and threat intelligence feeds.
- Risk Scoring: Vulnerabilities are scored based on multiple risk factors, including exploitability, asset criticality, and current threat landscape.
- Prioritization: Using the risk scores, the tools automatically rank vulnerabilities in order of importance.
- Actionable Insights: Teams receive recommendations on which vulnerabilities to address first, optimizing remediation efforts.
- Continuous Monitoring: RBVM tools provide ongoing assessment, ensuring the organization remains vigilant against new threats and vulnerabilities.
How to Implement A Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Program
Implementing a successful risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) program requires careful planning, clear priorities, and the tools to support continuous improvement. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building an effective RBVM strategy that helps your organization prioritize risk and enhance security.
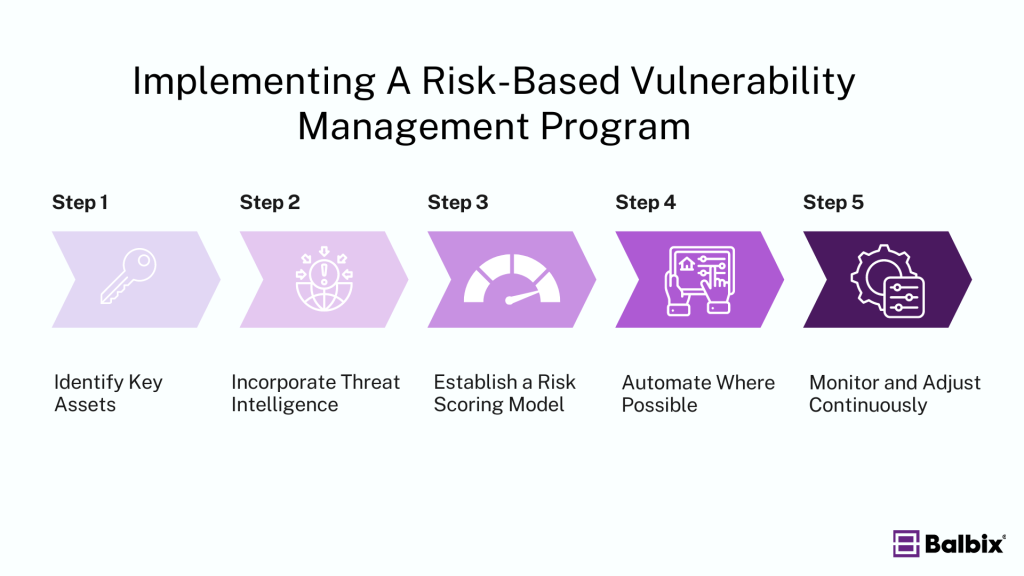
1. Identify Key Assets
The foundation of any RBVM program is a clear understanding of your organization’s most critical assets. These assets may include sensitive customer data, proprietary systems, intellectual property, or anything else that’s vital to the continuity of your business operations. The more critical an asset, the higher the risk if it’s compromised. Start by mapping out these key assets and assessing their importance to your business goals.
For example, Balbix’s AI-powered platform can help streamline this process by automatically discovering and classifying assets across your environment. It identifies these assets and evaluates their criticality, ensuring your risk-based strategy focuses on what’s truly important.
2. Incorporate Threat Intelligence
Real-time threat intelligence is crucial for staying ahead of emerging threats. Cyberattacks evolve rapidly, and a clear view of the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers can help your team focus on vulnerabilities actively being exploited. Effective threat intelligence enables security teams to prioritize fixes for vulnerabilities that could be weaponized in the wild, ensuring a more proactive approach to defense.
Stop Sabotaging Your Cybersecurity
Avoid the 11 common vulnerability management pitfalls

Balbix integrates up-to-the-minute threat intelligence, correlating external threat data with your internal risk landscape. This empowers security teams to prioritize existing vulnerabilities and is part of active threat campaigns, making your defense smarter and faster.
3. Establish a Risk Scoring Model
A critical step in RBVM is establishing a risk-scoring system reflecting the potential impact of vulnerabilities on your business. This involves assessing factors such as:
- Asset criticality: How essential the asset is to your organization.
- Exploitability: The likelihood that attackers can exploit a vulnerability.
- Business impact: The potential damage if the asset is compromised (e.g., financial loss, reputational damage, regulatory penalties).
Balbix quantifies risk in financial terms, which simplifies decision-making for security and business leaders. By understanding the dollar impact of each vulnerability, teams can prioritize remediation efforts based on which vulnerabilities present the most significant risk to the organization.
4. Automate Where Possible
Automation is key to scaling and maintaining an effective RBVM program. With the sheer volume of vulnerabilities that modern organizations face, manual processes are no longer sustainable. Automation helps security teams identify, assess, and prioritize vulnerabilities, ensuring quicker response times and reduced human error.
Balbix automates vulnerability detection, assessment, and prioritization using AI models that continually analyze and correlate data across your security ecosystem. This allows teams to focus on remediating high-risk vulnerabilities rather than being bogged down by manual sorting and assessment tasks. Balbix’s platform automatically recommends Next Best Actions, providing clear, actionable steps to mitigate risk.
5. Monitor and Adjust Continuously
Cybersecurity is dynamic, and your RBVM program should be, too. As new vulnerabilities and threats emerge, it’s crucial to continuously monitor your program’s performance and adjust your risk model as needed. Regularly revisiting asset inventories, updating threat intelligence, and refining risk scoring models ensures your security efforts align with the current risk landscape.
Balbix enables continuous monitoring of your risk posture, providing real-time visibility into how vulnerabilities and threats evolve over time. Its AI-powered insights help you adjust your program in real-time, ensuring that your security efforts always focus on the highest risks.
By following these steps and leveraging platforms like Balbix, your organization can build a robust risk-based vulnerability management program. Balbix’s AI-powered capabilities, automated workflows, and risk quantification in monetary terms make it easier for security teams to focus on the most pressing risks, streamline remediation, and continuously improve their security posture.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does RBVM differ from traditional vulnerability management approaches?
-
Risk-based vulnerability Management (RBVM) prioritizes vulnerabilities based on the risk they pose to an organization, unlike traditional methods that might treat all vulnerabilities equally. This means that instead of trying to fix every single security issue,
RBVM helps identify and address the most critical ones first, based on their potential impact. This approach ensures that resources are allocated more effectively to protect against significant threats.
- What are the main components or steps involved in implementing an RBVM program?
-
Implementing an RBVM (Risk-Based Vulnerability Management) program involves several key steps.
- First, you need to identify and assess the risks present in your IT environment.
- Next, prioritize these vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation.
- Then, address these vulnerabilities through remediation or mitigation strategies.
- Finally, continuously monitor and adapt your approach as new risks emerge.
This ongoing process helps ensure your systems remain secure against evolving threats.
- What are the benefits of adopting an RBVM approach for an organization?
-
Adopting a Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) approach helps an organization focus on the most critical security weaknesses first, making its defense efforts more efficient and effective. It allows for better resource allocation, ensuring that the most significant risks are addressed promptly.
- How can an organization prioritize vulnerabilities effectively using RBVM?
-
An organization can effectively prioritize vulnerabilities using Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) by first identifying and assessing the risks posed by different vulnerabilities. This involves evaluating how likely each vulnerability is to be exploited and its potential impact on the organization.
RBVM then ranks these vulnerabilities based on their risk level, allowing the organization to focus on fixing the most critical issues first. This approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, addressing the biggest threats to the organization’s security.