Vulnerability management is critical to cybersecurity, but traditional methods can be slow, error-prone, and difficult to scale. With today’s increasing attack surfaces and complex networks, organizations need an automated solution to keep pace with evolving threats.
This article will explore how automating vulnerability management can enhance security posture, reduce manual workloads, and improve response times. We’ll also cover best practices to ensure your automated vulnerability management system works efficiently.
What is Automated Vulnerability Management?
Automated vulnerability management continuously identifies, assesses, prioritizes, and remediates security issues with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional vulnerability management, which requires manual scans and prioritization, automation streamlines these processes, allowing security teams to focus on high-priority tasks.
Automation addresses challenges posed by traditional methods, such as slow response times, incomplete asset inventory, and manual vulnerability prioritization, by continuously monitoring systems and automatically generating remediation actions.
Key Benefits of Automating Vulnerability Management
1. Faster Response Times
Automating vulnerability management allows for real-time detection of vulnerabilities, significantly reducing the time it takes to identify and address threats.
2. Accurate Prioritization of Vulnerabilities
An automated system can evaluate vulnerabilities based on risk factors like asset criticality, exposure level, and threat intelligence, ensuring the most critical issues are fixed first.
3. Reduced Human Error
By automating tasks like vulnerability discovery and remediation, organizations minimize the chances of oversight or mistakes commonly occurring with manual processes.
4. Improved Efficiency
Automation helps security teams work more efficiently by automating repetitive tasks like scanning and patch deployment, freeing up resources to focus on strategic initiatives.
5. Comprehensive Asset Inventory
Automated vulnerability management tools maintain an up-to-date inventory of all assets, including devices, cloud services, and third-party components, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
Challenges with Traditional Vulnerability Management
1. Manual Processes
Traditional vulnerability management relies heavily on manual processes, such as setting up scans, prioritizing results, and dispatching fixes. This can lead to delays in addressing critical vulnerabilities and increases the risk of human error.
2. Inconsistent Asset Inventory
Many organizations need help with manually maintaining an asset inventory. Important assets may be missed or misclassified, increasing the risk of exposure.
3. Limited Real-Time Coverage
Without continuous monitoring, traditional methods often leave organizations with outdated vulnerability data, making it difficult to respond to new threats promptly.
4. Inefficient Vulnerability Prioritization
Traditional vulnerability management struggles with prioritizing risks efficiently, often leading to low-priority issues being prioritized while more critical vulnerabilities remain unaddressed.
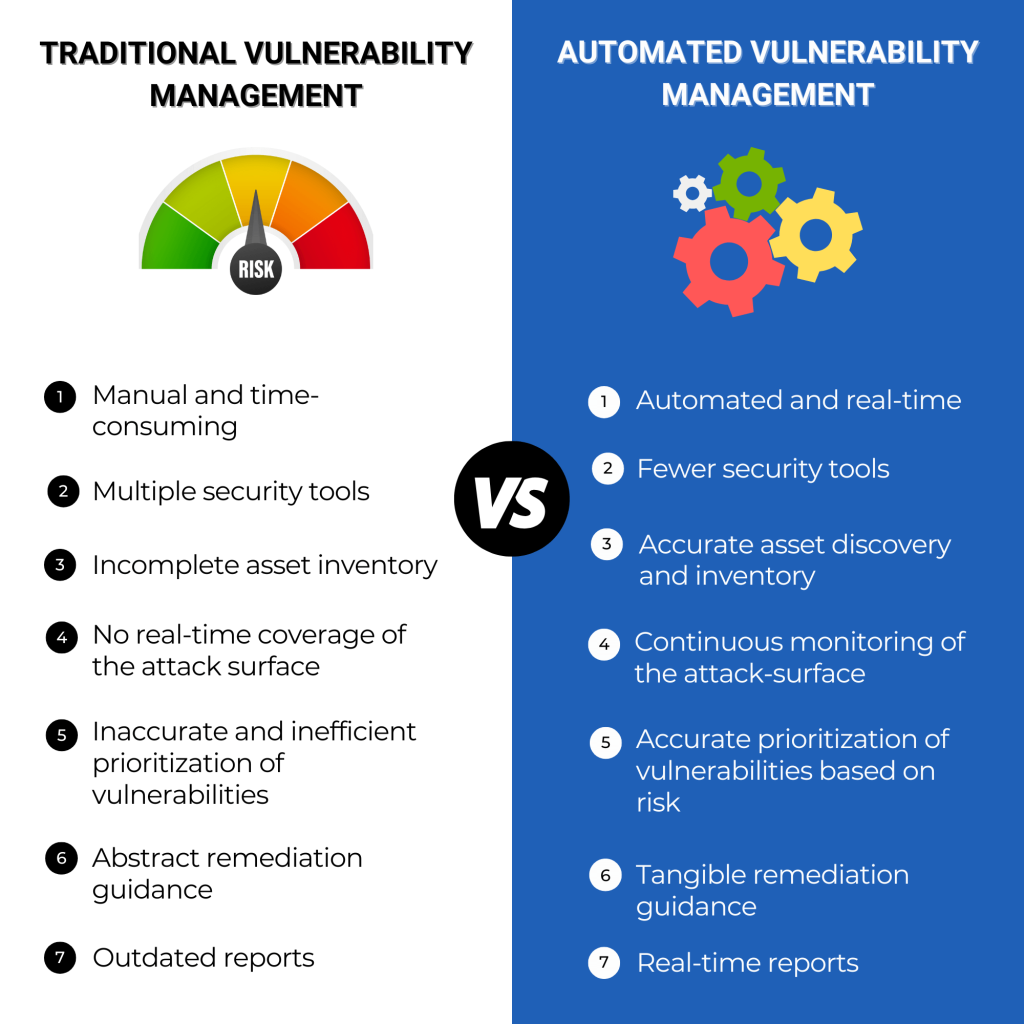
We explain how automated vulnerability management is different from traditional vulnerability management in the chart below:
How to Implement and Optimize Automated Vulnerability Management
Automating vulnerability management is a game-changer for organizations looking to enhance security, but it needs to be done thoughtfully. Here’s a step-by-step guide with some best practices to ensure your automation strategy delivers maximum value:
1. Build a Unified Asset Inventory
Continuously gather data from your IT and cybersecurity tools into one unified system. This consolidated view of your attack surface will be the foundation of your automated system, allowing it to monitor and assess vulnerabilities across your entire network effectively.
2. Incorporate Business Context
Map your assets to business functions and risk owners to enhance decision-making. Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on asset criticality, business impact, and exposure ensures you focus on the most common threats. By adding this context, automation becomes more accurate and impactful.
3. Continuously Monitor for Vulnerabilities
Your automated system should continuously scan assets for new vulnerabilities while monitoring existing ones. With real-time monitoring, you ensure that vulnerabilities are quickly identified and no threats slip through the cracks.
Stop Sabotaging Your Cybersecurity
Avoid the 11 common vulnerability management pitfalls

4. Automate Prioritization and Remediation
Use risk-based prioritization to tackle vulnerabilities based on severity, exposure, and business impact—not just traditional severity scores. Automated workflows can dispatch and track remediation steps, making the process more efficient and reducing the time to patch critical issues.
5. Test and Verify Patches
Before deploying patches, ensure they’ve been adequately tested to avoid instability or unintended side effects. Automated tools can help verify that patches are applied correctly and that vulnerabilities are fully remediated, giving you confidence in your fixes.
6. Generate Real-Time Reports
Automated tools can provide real-time reports, offering insights into your current security posture, the effectiveness of remediation efforts, and vulnerability trends. These reports are key for tracking progress and making data-driven decisions about future actions.
Best Practices to Optimize Automation
- Ingest Data from Multiple Sources: Combine data from internal and external sources to create a holistic view of your vulnerabilities and threats.
- Continually update your asset inventory to prevent it from becoming stale and out of date. Align this comprehensive asset inventory with your business functions.
- Leverage Risk-Based Prioritization: Focus on vulnerabilities that pose the highest risk based on real-time factors like asset exposure, business impact, and threat intelligence.
- Automate Patching and Remediation: Streamline patching efforts by automating patch deployment and remediation tracking, ensuring quick fixes for vulnerabilities.
- Customize Dashboards for Specific Roles: Tailor dashboards to your team’s needs, offering role-specific insights that empower security analysts, IT operations, and other key stakeholders to take targeted actions.
Why Automate Vulnerability Management with Balbix?
Balbix’s risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) platform offers a comprehensive, automated solution that simplifies vulnerability management and reduces cyber risk. With Balbix, organizations can:
- Automatically discover and inventory all assets, including cloud and third-party components.
- Identify vulnerabilities beyond traditional CVEs, such as misconfigurations and compliance violations.
- Continuously prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities based on asset criticality and business context.
- Automate the creation of remediation tickets and track progress in real-time.
Balbix’s platform helps organizations automate their vulnerability management processes, providing real-time visibility, prioritization, and remediation. With the right tools and best practices, automating vulnerability management can significantly enhance your organization’s security posture.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the main advantage of automating vulnerability management?
-
Automating vulnerability management reduces manual tasks, improves response times, and provides continuous visibility into vulnerabilities.
- How does automated vulnerability management prioritize threats?
-
Automated systems prioritize threats based on risk factors like asset criticality, exposure, and threat intelligence rather than just severity scores.
- Can automated systems handle patching?
-
Yes, automated systems can automate remediation tasks to deploy patches and verify their effectiveness, reducing the time to remediate vulnerabilities.