Understanding how attackers operate is half the battle in cybersecurity. As threats become more advanced and persistent, a structured approach to tracking, mapping, and neutralizing them is critical. The MITRE ATT&CK framework provides security professionals with a comprehensive defense system against adversarial tactics.
This article explores ATT&CK not just as a knowledge base but as a dynamic foundation for measurable, repeatable, and adversary-focused detection. We’ll explore how to move from theoretical coverage to practical implementation, how to use ATT&CK across red and blue teams, and why understanding technique-level nuances—like data sources, sub-techniques, and contextual metadata—is key to building effective detection strategies.
What is the MITRE ATT&CK Framework?
MITRE ATT&CK (Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge) is a curated knowledge base of adversary behaviors based on real-world observations. Each ATT&CK matrix (Enterprise, Mobile, ICS, Cloud) categorizes techniques and sub-techniques according to the attacker’s tactical objectives, such as initial access, persistence, or lateral movement.
Unlike traditional indicators of compromise (IOCs) focusing on endpoints or artifacts, ATT&CK emphasizes behavioral patterns—how attackers operate, not just what they leave behind. This approach allows defenders to build resilient, context-aware detections that aren’t easily bypassed by changes in tooling or infrastructure.
Here are three key aspects of the framework:
- Adversary Perspective: Unlike traditional defense-focused models, ATT&CK emphasizes understanding the attacker’s mindset and tactics.
- Standardized Vocabulary: It offers a common language for describing threats, making collaboration across teams easier.
- Post-compromise Focus: While most security models focus on preventing breaches, ATT&CK maps tactics and techniques attackers use after gaining access.
The framework empowers organizations to proactively hunt threats, fine-tune defenses, and test incident responses against real-world attack patterns.
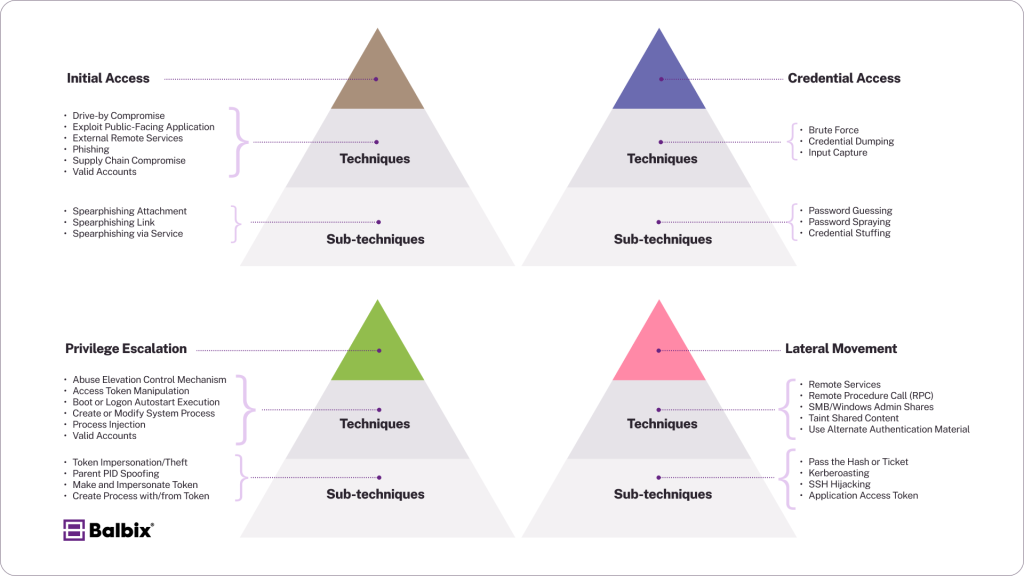
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
ATT&CK decomposes adversary behavior into three hierarchical levels:
- Tactics: The why—the adversary’s goal (e.g., Credential Access).
- Techniques: The how—a specific way to achieve a tactic (e.g., Brute Force).
- Sub-techniques: A more granular variant of a technique (e.g., Password Guessing).
Each technique entry includes metadata such as detection recommendations, associated mitigations, applicable platforms, and references to real-world threat groups that have employed it.
Here are four examples of TTPs in action for specific threats:
Read more about Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs).
Understanding the MITRE ATT&CK Matrices
The MITRE ATT&CK framework consists of multiple matrices, each tailored to a specific domain:
1. Enterprise ATT&CK Matrix
The Enterprise ATT&CK matrix covers tactics and techniques adversaries use to attack enterprise networks, including various platforms like Windows, macOS, Linux, Azure AD, and SaaS environments. It is the most widely used matrix, providing detailed insights into how adversaries compromise and operate within an enterprise.
2. Mobile ATT&CK Matrix
The Mobile ATT&CK matrix focuses on threats to mobile devices. It highlights tactics and techniques for iOS and Android platforms. It also covers methods attackers use without requiring physical access to the device, such as exploiting mobile apps or network services.
3. ICS ATT&CK Matrix
The ICS ATT&CK matrix is designed for industrial control systems in the energy, manufacturing, and utilities sectors. This matrix includes tactics and techniques unique to ICS environments, such as manipulating control system devices or exploiting industrial protocols.
4. Pre-ATT&CK Matrix
The scope of MITRE ATT&CK also expands beyond technology domains with PRE-ATT&CK. PRE-ATT&CK documents adversary activities such as gathering requirements, performing reconnaissance, and preparing for an attack before gaining access to a network.
It focuses on the early stages of an attack, independent of specific technologies, by modeling the strategies and tactics adversaries use to target and plan attacks against organizations before they penetrate a network. This helps organizations anticipate and defend against threats earlier in the attack lifecycle.
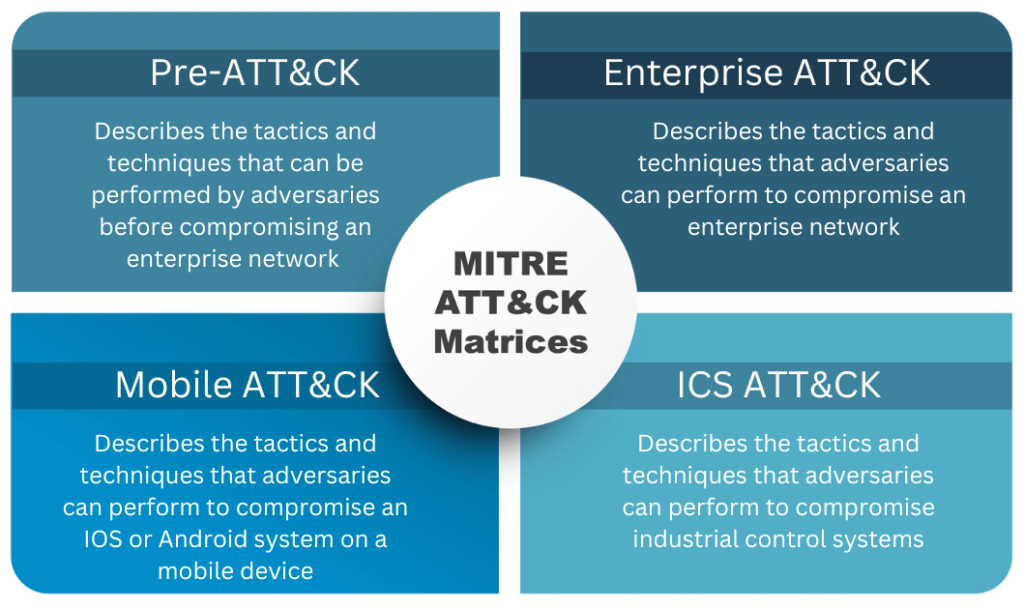
Each matrix provides detailed descriptions of attacker tactics, techniques and common knowledge. It also outlines the detection and mitigation, if applicable, and provides examples of real-world use cases.
Why MITRE ATT&CK Matters for Security Operations
MITRE ATT&CK enables defenders to:
- Design coverage-aware detections: Map analytics to specific TTPs and identify detection gaps.
- Align detection with threat intel: Translate threat reports into actionable detection requirements.
- Benchmark SOC capabilities: Assess the maturity of detection across tactics and techniques.
- Enable red-blue team collaboration: Use ATT&CK as a common vocabulary during purple team exercises.
- Drive threat-informed defense: Prioritize detections based on the most likely or most impactful threats.
Common Misunderstandings About MITRE ATT&CK
Despite its utility, MITRE ATT&CK is often misapplied:
- “ATT&CK coverage” ≠ detection coverage: Listing a technique doesn’t mean you can detect it. Coverage requires telemetry, enrichment, and validated analytics.
- IOCs are not TTPs: Indicators like hashes or IPs are fragile. ATT&CK focuses on behavior, which is harder for adversaries to change.
- Mapping alerts is insufficient: ATT&CK should inform detection logic, not just retroactively label alerts.
- Not all TTPs are equal. Some techniques are more common or impactful based on threat modeling and industry context.
How to Operationalize MITRE ATT&CK
- Baseline Your Visibility: Identify which data sources are available in your environment (e.g., process execution logs, PowerShell logs, network flow data). Map these to the data sources recommended by ATT&CK for detecting relevant techniques.
- Map Existing Detections to ATT&CK: Annotate existing detections with associated ATT&CK techniques/sub-techniques. Use this to identify gaps, redundancies, or incomplete coverage.
- Build Detection-as-Code: Codify detection rules using languages like Sigma, and include ATT&CK mappings in the rule metadata. This makes your detections portable, version-controlled, and auditable.
- Validate with Purple Teaming: Use red team simulations or tools like Atomic Red Team to emulate specific ATT&CK techniques and validate your detections. This ensures your coverage is real, not just theoretical.
- Prioritize by Threat Intelligence and Risk: Focus on techniques used by threat actors relevant to your sector. Use threat modeling and MITRE ATT&CK Navigator layers to prioritize high-value TTPs.
- Continuously Improve: ATT&CK is updated regularly, so should your detections. Regularly review updates, adversary emulation plans, and telemetry capabilities to maintain coverage.
MITRE ATT&CK Tools and Resources
Several tools are built around the MITRE ATT&CK framework to help organizations operationalize it:
- ATT&CK Navigator: A visualization tool that helps users navigate and analyze the various matrices.
- MITRE Cyber Analytics Repository (CAR): A resource that provides analytics for detecting adversarial behaviors documented in the ATT&CK framework.
- Caldera: An automated red-teaming tool that simulates adversarial behavior based on ATT&CK techniques.
- Red Canary Atomic Red Team: An open-source tool that allows organizations to test their defenses against specific ATT&CK techniques.
MITRE ATT&CK vs. Cyber Kill Chain
The Cyber Kill Chain, developed by Lockheed Martin, is another widely used model for understanding cyberattacks. However, there are fundamental differences between it and the MITRE ATT&CK framework:
- Focus: While the Cyber Kill Chain emphasizes the pre-attack phases, ATT&CK focuses on the post-compromise behaviors of adversaries.
- Granularity: ATT&CK provides a more detailed view of adversarial techniques, making pinpointing specific behaviors and responses easier.
Cyber Kill Chain did not have a high adoption rate due to the lack of detail and flexibility, making it suitable for High-level understanding and disrupting attacks during their lifecycle; however, for organizations seeking a deep understanding of adversary behavior and a comprehensive approach to defense, MITRE ATT&CK is preferred.
| MITRE ATT&CK | Cyber Kill Chain | |
| Origin | MITRE | Lockheed Martin |
| Focus | Detailed adversary tactics and techniques | Stages of an attack lifecycle |
| Structure | Non-linear tactics and techniques | Linear, seven stages of an attack |
| Granularity | High, detailed techniques and sub-techniques | Generalized, focuses on broader stages |
| Application | Threat detection, red teaming, forensic analysis | Threat intelligence, incident response |
| Lifecycle Coverage | Comprehensive, from initial access to impact | Focus on external network-based attacks |
| Used by | Blue and Red Teams, Threat Hunters, IR Teams | Threat Intelligence Analysts, Incident Responders |
Final Thoughts
MITRE ATT&CK is not just a classification system—it’s a strategic asset for defenders who want to build resilient, threat-informed security programs. But to extract real value, you must treat ATT&CK as more than a static checklist. Operationalizing ATT&CK means driving every phase of the detection lifecycle—from telemetry strategy to detection engineering to validation.
Used correctly, ATT&CK helps defenders shift from reactive defense to proactive detection, reducing adversaries’ dwell time and increasing the cost of evasion. It’s not just about what the attacker did. It’s about being ready for what they’ll do next.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the MITRE ATT&CK Framework used for?
-
MITRE ATT&CK maps and classifies adversary behaviors, helping defenders understand and detect attack techniques based on real-world intelligence rather than static indicators.
- How is ATT&CK different from traditional IOCs?
-
Unlike IOCs (e.g., IPs or file hashes), ATT&CK focuses on behavioral patterns—tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs)—which are more resilient and harder for attackers to evade.
- Can mapping detections to ATT&CK improve SOC performance?
-
Yes. Mapping helps security teams identify coverage gaps, prioritize detection efforts, and benchmark their capabilities against specific adversarial behaviors.
- How has the MITRE ATT&CK Framework evolved since its inception?
-
Developed in 2013 and made public in 2015, the MITRE ATT&CK Framework has continuously evolved. Key milestones include the addition of macOS and Linux coverage in 2017, the introduction of the Mobile ATT&CK Matrix and ATT&CK for Cloud, and the expansion to include sub-techniques in 2020 for more granular documentation of adversarial behaviors.
- Why is the MITRE ATT&CK Framework important for cybersecurity?
-
The MITRE ATT&CK Framework is critical for cybersecurity as it provides a common language and systematic approach for documenting and sharing information on cyber threats. This enables organizations to better prepare for, detect, and respond to cyberattacks, improving overall security posture and resilience against threats.
- How often is MITRE ATT&CK updated?
-
MITRE updates the ATT&CK framework regularly to reflect new techniques and evolving threat behaviors. Staying current is crucial for maintaining effective detection strategies.