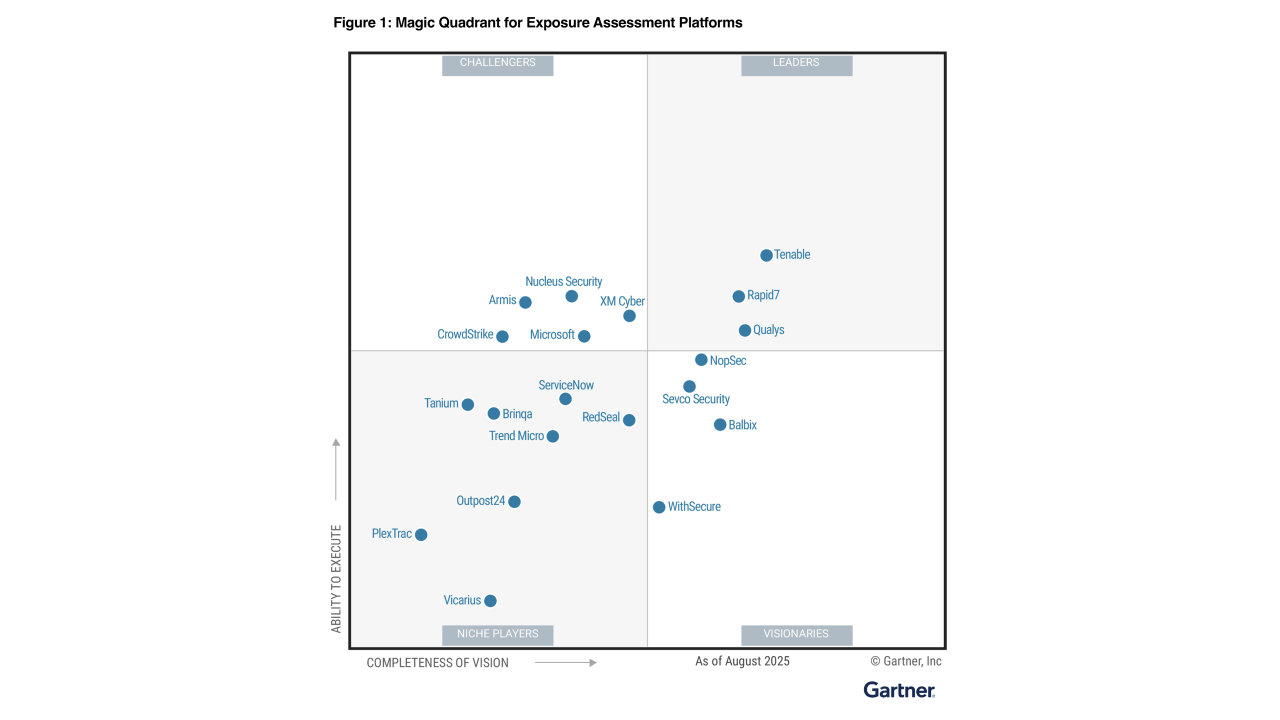
Cybersecurity threats evolve faster than traditional defenses can adapt. Organizations face hundreds of vulnerabilities daily, but not all pose an immediate risk. How do you determine which ones matter most? How do you defend against tomorrow’s threats—not just today’s? This is where Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) steps in.
CTEM shifts cybersecurity from reactive to proactive. Continuously identifying, assessing, and mitigating threats ensures that your organization stays one step ahead of attackers rather than reacting once breaches occur. If you’re an IT Manager, Security Professional, or CISO, understanding and adopting CTEM could massively strengthen your organization’s security posture.
This article unpacks everything you need to know about CTEM—including its, why it matters, its five-stage framework, tools, and how it compares to other security methodologies.
What is CTEM?
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) monitors, assesses, and addresses real-time vulnerabilities across your attack surface. At its core, Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is an advanced, proactive cybersecurity approach.
Unlike traditional vulnerability management—which conducts periodic scans and reacts to detected vulnerabilities long after they appear—CTEM operates as an ongoing process, leaving no room for blind spots or delays.
Gartner, a global research and advisory firm, has been instrumental in defining and promoting CTEM. Gartner states, “Continuous threat exposure management is a pragmatic and effective systemic approach to continuously refine priorities and walk the tightrope between two modern security realities.”
Key Features of CTEM:
- Proactive Monitoring: Continuous scanning and assessment of vulnerabilities across your systems to identify potential threats before they become critical issues. This real-time monitoring ensures you stay one step ahead of potential attacks.
- Prioritized Threat Management: This approach focuses resources on addressing the most critical risks to your business, ensuring that your team spends time and effort where it matters most. By ranking threats based on their severity, CTEM helps manage risks efficiently.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Integrates threat management with your organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that cybersecurity efforts directly support and protect your key business priorities and operations.
Why CTEM Matters in Cybersecurity
Traditional cybersecurity strategies are no longer enough. Periodic vulnerability assessments and slow remediation processes are ill-equipped to address today’s dynamic threat environment.
Here’s why CTEM has become a game-changer:
The Dynamic Nature of Threats
Cyber threats constantly evolve, with ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits becoming more sophisticated. A “set it and forget it” approach to cybersecurity leaves organizations unprepared. CTEM provides the continuous oversight needed to adapt to these shifting risks.
Focus on Exposure Management
Where older frameworks aim to react to security incidents, CTEM takes a preventive approach. By continuously managing exposures—not just waiting for breaches to occur—CTEM significantly reduces the chances of successful cyberattacks.
Read our comprehensive and detailed guide to exposure management to learn more about this proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Relatable Benefits for Your Business
Thanks to proactive threat management, organizations implementing Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) experience fewer security incidents. They also improve operational efficiency by focusing resources on the most critical risks rather than spreading efforts too thin.
Additionally, preventing breaches safeguards customer trust and protects the organization’s brand reputation.
The Five Stages of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
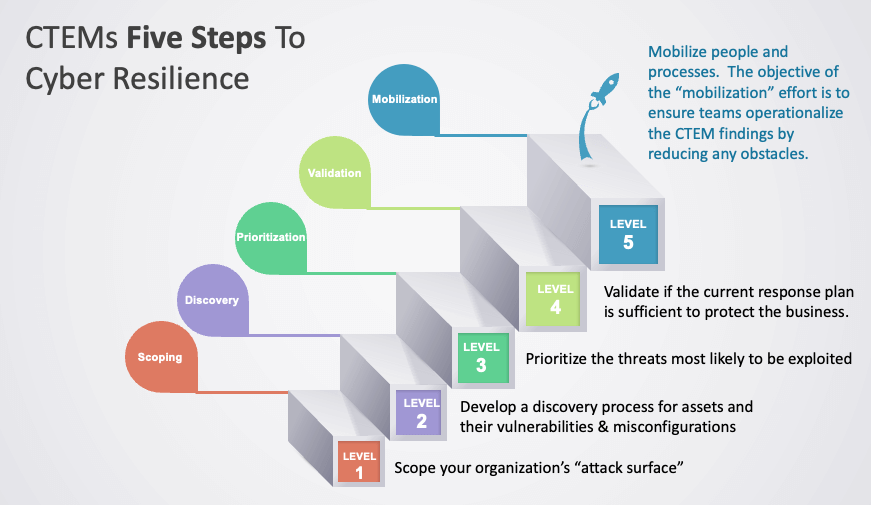
Implementing Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) requires a structured, five-stage process to proactively identify, prioritize, and address security risks. Each stage strengthens your organization’s security posture, ensuring you stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Let’s explore how each stage contributes to a resilient security strategy:
1. Scoping: Defining Security Priorities
CTEM begins with scoping—identifying critical assets and aligning security goals with business objectives to ensure resources are used efficiently to protect what matters most. For example, a tech startup may prioritize securing customer data, intellectual property, and proprietary algorithms to make strategic and effective security investments.
Key considerations include assessing risk tolerance, business priorities, and the potential impact of data breaches. Clear scoping is essential to prevent wasted resources and ensure cybersecurity efforts directly support business needs.
2. Discovery: Identifying Vulnerabilities
Once the scope is defined, the next step is discovering vulnerabilities across networks, applications, cloud environments, and IoT devices through automated scanning and manual assessments.
Vulnerability scanning tools efficiently scan for vulnerabilities, while manual audits help identify issues that automated tools might miss. It’s also crucial to map all digital assets, including unmanaged and shadow IT systems, to eliminate hidden security gaps.
Get tips and strategies for selecting a vulnerability management tool and learn about the top VM tools.
3. Prioritization: Focusing on the Most Critical Threats
Not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk, making prioritization essential to ensure security teams address the most dangerous threats first. By focusing on high-risk vulnerabilities, organizations can reduce the likelihood of breaches while maximizing efficiency and impact.
Tracking metrics like Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) helps measure how quickly critical vulnerabilities are resolved while leveraging threat intelligence, which allows teams to anticipate attacker tactics and refine their prioritization strategies.
Addressing high-risk vulnerabilities first prevents costly breaches and ensures security resources are used effectively.
4. Validation: Ensuring Effective Remediation
After addressing vulnerabilities, validation is crucial to ensure that fixes are effective and haven’t introduced new security gaps. Penetration testing tools or manual red team exercises simulate real-world attacks to test defenses, while validation should also include checking system configurations to prevent unintended risks.
Without this step, unresolved security gaps could linger, creating a false sense of security. Organizations can confirm their defenses are truly effective by thoroughly validating remediation efforts.
5. Mobilization: Maintaining Continuous Security
Cybersecurity is an ongoing effort, and mobilization ensures that CTEM remains a continuous, adaptive process that evolves with emerging threats. This requires regularly updating security processes, tools, and training while fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness and resilience.
Strategies like frequent threat simulations and tabletop exercises help test and refine incident response plans, ensuring teams are prepared for real-world attacks. Since threats constantly evolve, static defenses won’t suffice—taking a proactive, continuous approach helps organizations stay ahead of attackers.
CTEM vs. ASM and SIEM
CTEM is often compared to other cybersecurity approaches like Attack Surface Management (ASM) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), but it serves a distinct purpose.
CTEM vs. ASM (Attack Surface Management)
ASM focuses on identifying all possible entry points for attackers, providing visibility into an organization’s attack surface, but it doesn’t actively manage exposures. CTEM goes beyond surface mapping by continuously reducing exposure across all assets, integrating intelligence with direct action.
CTEM vs. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
On the other hand, SIEM platforms excel at detecting and responding to active incidents but operate reactively, addressing threats only after they emerge. CTEM mitigates risks proactively, reducing the number of alerts SIEM systems must handle.
When used together, CTEM and SIEM create a stronger, more balanced security posture, ensuring that organizations are not just reacting to threats but actively minimizing their risk before attackers can exploit vulnerabilities.
The Benefits of CTEM
Let’s explore the key benefits of Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), and how it enhances proactive risk management, resource efficiency, security posture, and continuous improvement.
Proactive Risk Management
With CTEM, businesses can identify and address vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. Early threat detection provides the opportunity to implement preventive measures, reducing the likelihood of costly breaches and ensuring critical systems remain secure.
Efficient Resource Allocation
CTEM prioritizes risks based on their potential impact, helping organizations focus their time, money, and efforts on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first. This targeted approach maximizes the effectiveness of security measures and frees up resources to invest in other strategic initiatives or innovation areas.
Enhanced Security Posture
CTEM strengthens an organization’s defenses against emerging risks by continuously monitoring and assessing potential threats. This approach minimizes the overall attack surface and ensures that businesses are better prepared to handle evolving cybersecurity challenges, building resilience for the long term.
Continuous Improvement
CTEM fosters a culture of constant learning and adaptation. By regularly evaluating security strategies and integrating feedback, businesses can ensure that their security evolution stays aligned with organizational growth and technological advancements. This continuous improvement drives innovation and keeps security measures relevant and effective.
Metrics such as Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) clearly show how well a CTEM strategy performs. These measurable results demonstrate the effectiveness of a proactive security approach and help communicate value and progress to stakeholders, reinforcing trust and accountability.
Build a Stronger Security Strategy with CTEM
Adopting Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) requires the right tools to support its continuous, proactive approach. Balbix is an AI-powered exposure management platform that helps organizations implement CTEM effectively by providing real-time vulnerability assessments, business-impact prioritization, and predictive risk modeling. Security teams rely on Balbix for its clear visual reports and automation-driven insights, enabling them to reduce exposure and confidently strengthen their security posture.
By integrating CTEM into your cybersecurity strategy, you can move beyond reactive security measures and take a proactive stance against evolving threats. With Balbix, your organization can seamlessly transition to a smarter, more resilient security approach—ensuring risks are managed before they become breaches.
Learn more about exposure management tools and how to choose the right one for your organization.
From Linear to Parallel: How Balbix Powers CTEM at Scale
Most security programs still treat cyber risk like a sequential checklist — first find every asset, then map every vulnerability, then start fixing. But as Gaurav Banga, Balbix CEO, notes, “Cyber risk isn’t a backlog problem. It’s a parallel processing problem.”
In today’s dynamic threat environment, CTEM can’t run in sequence — it has to run in parallel across three continuous tracks that reinforce one another:
Track 1: Burndown on Known Exposures
Every enterprise already has a subset of assets with “good enough telemetry” — ownership known, controls mapped, vulnerabilities visible.
Balbix identifies this Good Telemetry Group in days, helping teams focus on what’s exploitable, business-critical, and high risk first. Within weeks, enterprises see measurable progress:
- 100% of critical exposures remediated
- Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR) under 5 days
- Up to 60% reduction in risk in the first 90 days
This early momentum builds board-level confidence and demonstrates immediate ROI from CTEM.
Track 2: Expanding Telemetry and Visibility
While remediation runs, Balbix drives telemetry enrichment across the broader environment — servers, apps, cloud, and IoT.
The platform shows exactly which signals matter most for exposure reduction, guiding enrichment projects that are time-bound and high-impact.
Enterprises typically see a 30%+ visibility increase within 60–90 days, dramatically expanding the universe of assets covered by CTEM.
Track 3: Continuous Exposure Management
Finally, CTEM becomes a continuous loop:
Ingest → Prioritize → Assign → Fix → Validate → Close.
Balbix automates this process with explainable risk scoring, SLA tracking, and closed-loop validation.
The result:
- New CVEs auto-assigned within a day
- ≥95% exposures closed within SLA
- ≥90% auto-routing to owners — no manual chasing
This parallel-track model turns CTEM from theory into execution — a living, measurable operating system for security.
Why Parallelism Wins
Running CTEM in parallel multiplies impact:
- Burndown delivers credibility and visible results.
- Expansion prevents blind spots from returning.
- Continuous management sustains resilience as threats evolve.
With Balbix, all three happen simultaneously — enabling enterprises to reduce exposure faster, prove progress to the board, and evolve toward a self-optimizing security posture.
CTEM isn’t just continuous. With Balbix, it’s concurrent.
? Request a demo to see how your organization can operationalize CTEM the Balbix way.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is CTEM in cybersecurity?
-
CTEM stands for Continuous Threat Exposure Management. It’s a proactive approach that continuously identifies, prioritizes and reduces cyber risk across an organization’s entire attack surface. This helps organizations stay ahead of threats instead of reacting after a breach.
- How does CTEM work?
-
CTEM follows a five-stage framework: scoping, discovery, prioritization, validation, and mobilization. This cycle helps organizations uncover exposures in real time, focus on the most critical risks, validate fixes, and continuously improve their security posture.
- Why is CTEM important?
-
CTEM helps businesses move from reactive to proactive security. Organizations can reduce risk, improve resource efficiency, and align cybersecurity with business goals by constantly managing exposures- not just reacting to incidents.
- What is the difference between CTEM and traditional vulnerability management?
-
Traditional vulnerability management relies on periodic scans and delayed remediation. CTEM, on the other hand, provides continuous visibility and prioritization, ensuring vulnerabilities are identified and addressed before they can be exploited.
- How is CTEM different from ASM and SIEM?
-
Attack Surface Management (ASM) maps vulnerabilities, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) responds to threats. CTEM complements both by proactively reducing exposures—closing security gaps before attackers can take advantage.