Data breaches have become an all-too-common threat. Businesses, organizations, and individuals face increasing risks as cybercriminals employ sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities to steal data and disrupt business operations. This article will explore what a data breach is, how it happens, the types of data targeted, and, most importantly, how to prevent it.
What Is a Data Breach?
A data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals access sensitive, confidential, or protected data. This data can include personal information, financial or health records, intellectual property, or other sensitive data elements. Breaches can lead to identity theft, financial losses, and damage to business reputation.
Data breaches can happen to any organization, regardless of size, making detection & prevention critical aspects of modern cybersecurity efforts.
How Does a Data Breach Occur?
Data breaches often exploit gaps in an organization’s security posture, combining human error, technical vulnerabilities, and advanced attack methods. Below are some of the most common ways breaches occur, with a closer look at the specific processes involved.
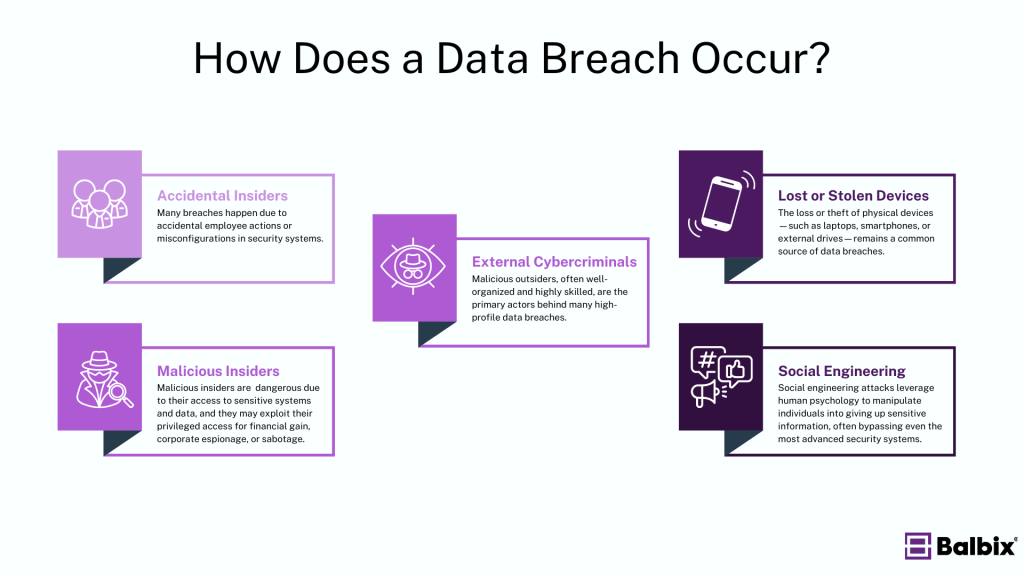
1. Accidental Insider Threats
Insider threats don’t always stem from malicious intent. Many breaches happen due to accidental employee actions or misconfigurations in security systems. For example:
- Misconfigured access controls in cloud environments can expose databases to the public internet, providing open access to sensitive information.
- Accidental sharing of sensitive files through unsecured email or cloud services can lead to data exposure.
- Weak password practices, such as reusing passwords across systems or failing to use multi-factor authentication (MFA), can allow attackers easy access to critical systems if one set of credentials is compromised.
2. Malicious Insiders
Malicious insiders are particularly dangerous due to their access to sensitive systems and data. These individuals may exploit their privileged access for financial gain, corporate espionage, or sabotage. Malicious insiders can:
- Exfiltrate data via external drives, email, or unauthorized cloud storage.
- Escalate privileges or turn off security controls, allowing broader and stealthier access to critical systems.
- Plant malware on internal systems to establish persistent access or disrupt operations.
3. External Cybercriminals
Malicious outsiders, often well-organized and highly skilled, are the primary actors behind many high-profile data breaches. These attackers use various techniques to infiltrate networks, including:
- Phishing: Crafting convincing emails or messages that trick employees into divulging credentials or downloading malware. Sophisticated phishing attacks can also target high-level executives in what’s known as spear phishing.
- Malware: Attackers deploy malicious software (e.g., ransomware, spyware, keyloggers) to infect devices and gain control over systems. Advanced forms of malware can evade detection by traditional antivirus solutions, often leveraging zero-day vulnerabilities or novel coding techniques to hide in plain sight
- Brute-force attacks: Cybercriminals use automated tools to try numerous password combinations until they find one that grants access to systems. This technique often succeeds due to weak & reused passwords or the lack of MFA.
4. Lost or Stolen Devices
The loss or theft of physical devices—such as laptops, smartphones, or external drives—remains a common source of data breaches. In many cases, these devices contain sensitive or unencrypted data, making it easier for attackers to access:
- Unencrypted data at rest can be easily extracted from a stolen device.
- Saved or weak credentials can bypass endpoint security solutions. If the device is linked to company networks, attackers could gain access to internal systems.
- No remote wipe capability means the company has no recourse to erase data once a device is out of its control.
5. Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks leverage human psychology to manipulate individuals into giving up sensitive information, often bypassing even the most advanced security systems. These attacks include:
- Phishing (Email or SMS): Attackers impersonate trusted entities, such as company executives or well-known brands, to trick employees into clicking malicious links or providing login credentials.
- Pretexting: Attackers create a fabricated scenario (e.g., posing as an IT support technician) to trick employees into revealing sensitive information or granting access to internal systems.
- Baiting and Quid Pro Quo: Attackers may offer something of value (e.g., a free download or reward) in exchange for sensitive information or system access.
What Information Gets Stolen in a Data Breach?
Attackers typically target data that can be monetized or leveraged for malicious purposes. Some of the most common targets include:
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Data such as names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and birth dates can be used for identity theft.
- Financial Information: Credit card numbers, bank account details, and payment information are often exploited for financial fraud.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Companies’ trade secrets, patents, and proprietary information are valuable assets for corporate espionage.
- Personal Health Information (PHI): Medical records contain sensitive information that can be used for identity fraud or blackmail.
- Login Credentials: Usernames, passwords, and access tokens can be sold or used to breach additional accounts.
Once attackers access this data, they can carry out fraud, identity theft, ransomware attacks, or even sell the information on the dark web.
The Damage of a Data Breach
A data breach can have a ripple effect, unleashing a cascade of consequences that disrupt individuals and organizations. The financial impact is often immediate and severe—businesses may face substantial costs for legal fees and regulatory fines. However, the problem may persist for longer, such as the continual expensive tasks of investigating and remediating the breach and managing long-term legal challenges like class-action lawsuits or even governmental inquiries.
But the damage extends beyond dollars. Harm to overall reputation is often harder to recover from, as customer trust—one of a company’s most valuable assets—can be shattered overnight, leading to lost business and long-term brand damage.
Meanwhile, operational disruption is common, particularly in the case of ransomware attacks that bring down critical systems, causing significant downtime and halting productivity. Compounding these issues, organizations will likely face steep regulatory penalties under data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA, further amplifying the financial and legal burden.
In the end, a data breach doesn’t just result in lost data—it inflicts lasting harm on every aspect of the business, from finances to operations to reputation.
How to Prevent a Data Breach
Preventing data breaches requires a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Following the steps below, businesses can minimize risk and strengthen their defense against attacks.
1. Implement Strong Access Controls
Limiting access to sensitive data ensures that only authorized personnel can view or interact with critical information. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of protection. Regularly review access permissions and revoke privileges when employees change roles or leave the company. Ensure system accounts, certificates, and access via API are also considered when evaluating “least privilege.”
2. Educate and Train Employees
Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches. Providing recurring cybersecurity training helps employees recognize threats like phishing and social engineering. Regularly update training to ensure all staff know the latest risks and best practices.
3. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Data encryption ensures that even if data is stolen or intercepted, it cannot be read without the proper decryption key. Encrypt data both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being sent).
4. Maintain Up-to-Date Software and Security Patches
Unpatched software vulnerabilities provide an easy way for cybercriminals to gain access to systems. Ensure that all software, including operating systems, is regularly updated to close security gaps. This includes company systems and employee devices if they are used for work purposes.
5. Use Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls help monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules. Meanwhile, IDS solutions can detect suspicious activity, assisting organizations to respond quickly to potential breaches.
6. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments
Regular risk assessments and security audits help identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Use these assessments to improve your security measures continuously and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
7. Secure Physical Devices
Implement policies to secure devices such as laptops, phones, and tablets. If devices are lost or stolen, employees must use encryption, strong passwords, and remote wipe capabilities. Disable external ports so portable drives cannot be used to exfiltrate data or install malware.
8. Monitor Network Traffic & System Logs
Set up real-time monitoring of network traffic & system logs to detect unusual activity. Early detection of potential breaches can help mitigate damage and respond more swiftly to threats.
9. Segment network traffic
Implement network segmentation to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems from unexpected environments. Ensure that lab and development networks do not have access to any production environments.
Final Thoughts
Preventing a data breach requires a comprehensive strategy, including technological solutions and employee education. By following these preventative measures, businesses can reduce risk, protect sensitive data, and maintain customer trust.
As a leader in exposure management, Balbix enables organizations to avoid potential breaches by providing continuous visibility into all assets, vulnerabilities, and risks across the attack surface. Using AI-driven insights, Balbix helps security teams prioritize the most critical risks based on business context so they can focus on the issues that matter most.
With automated risk quantification and real-time mitigation recommendations, Balbix empowers organizations to reduce their exposure to cyber threats and prevent breaches before they occur.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How can you protect yourself from a data breach?
-
Protecting yourself from a data breach means being proactive.
- Always keep your software updated to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Use strong, unique passwords for different accounts and consider a password manager to keep track of them.
- Enable two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
- Also, be cautious about your online information and regularly check your account statements for suspicious activity.
- Why do data breaches happen?
-
Data breaches often occur due to inadequate cybersecurity measures, human error, and sophisticated hacking techniques.
Companies might not update their software regularly, or employees might accidentally leak sensitive information.
Hackers also continually evolve their methods to exploit any vulnerability. It’s like a constant game of cat and mouse, where both sides try to outsmart each other.
- How do I report a data breach?
-
If you’ve encountered a data breach, it’s important to act swiftly. Start by contacting the organization involved to report the breach. You should also inform relevant regulatory bodies or authorities, as laws vary by region.
Don’t forget to keep a record of all communications for your reference. Taking these steps helps manage the situation responsibly and contributes to better data security


