Cyberattacks are no longer rare events or one-off crises; they are a regular occurrence in today’s digital landscape. With daily headlines announcing ransomware payouts, data breaches, and regulatory fines, proactive cyber risk management has never been more crucial.
One critical tool for managing this risk is cyber insurance. But what exactly does it do? Does it cover every cyber threat, and who really needs it?
This article explores the fundamentals of cyber insurance, the types of coverage it offers, and why it should be part of your cyber risk strategy.
What Is Cyber Insurance?
At its core, cyber insurance is a safety net for the financial fallout of cyber incidents. Cyber insurance helps businesses manage the costs associated with events like ransomware attacks, data breaches, or operational downtime.
Unlike traditional liability or property insurance, cyber insurance is specifically designed to address cyber risks. This includes the company’s direct losses (think lost revenue, recovery expenses) and potential legal liabilities (like regulatory fines).
Quick Note: Cyber insurance is sometimes called cybersecurity liability insurance. Both terms mean the same thing.
Why is the demand for cyber insurance growing?
The exponential growth in data and reliance on digital infrastructure has created a larger attack surface for threat actors. Over the past decade, new regulations like GDPR and CCPA have also heightened the financial and reputational stakes for businesses suffering a breach.
For IT professionals and security leaders, cyber insurance isn’t just a “nice-to-have” anymore; it’s a financial safeguard in cases where even the best defenses can be breached.
What Does Cyber Insurance Cover?
Cyber insurance is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Policies and coverage vary widely between insurers. However, coverage typically falls into three categories, which can often be bundled together.
1. First-Party Coverage
This type of coverage handles losses that directly impact your business. It generally includes:
- Data recovery costs: For restoring lost or corrupted data after a cyberattack.
- Business interruption: Compensation for revenue lost due to operational downtime caused by an incident.
- Ransom payments: Covers payments made to threat actors in ransomware situations.
- Incident response services: Access to forensic analysts and cybersecurity experts to investigate the breach.
- Crisis communication support: Help with PR efforts to manage reputation following an incident.
2. Third-Party Coverage
Third-party coverage protects your business from the legal and compliance fallout of an attack, such as:
- Legal defense costs and settlements: For lawsuits brought by customers, partners, or vendors impacted by the attack.
- Regulatory fines: Covers penalties arising from non-compliance with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Customer notifications: Costs for notifying affected parties when their data has been compromised.
3. Cybercrime-Specific Coverage
With the rise of cybercrime tactics such as phishing and social engineering, insurers now offer niche coverages tailored to these threats, such as:
- Social engineering fraud: Coverage for losses from scams involving tricked employees.
- Wire transfer fraud: Reimbursement for fraudulent or misdirected transactions.
- Phishing-based financial loss: Recovering stolen funds from targeted phishing attacks.
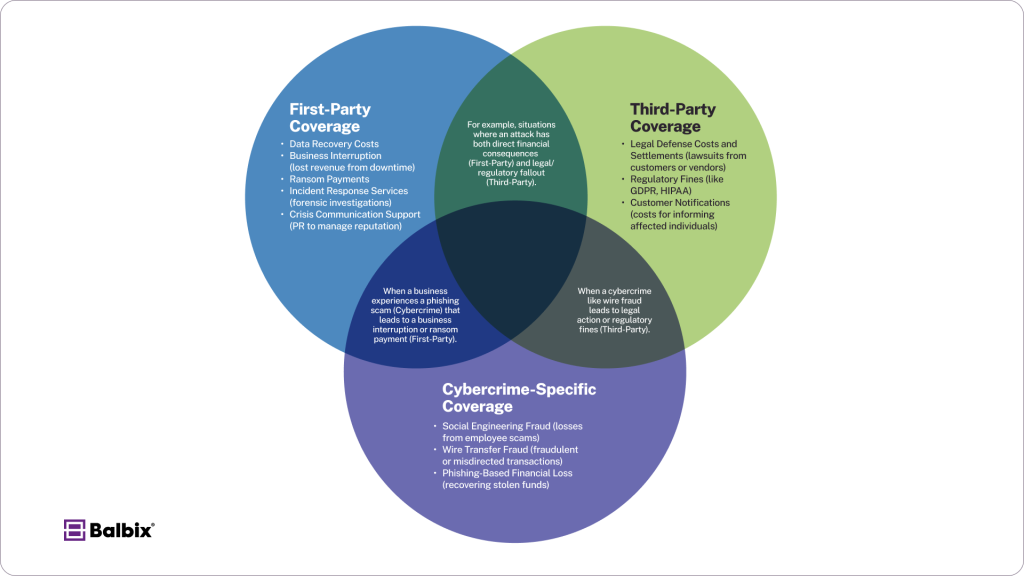
It’s important to note that not all policies include cybercrime coverage as a standard feature. Businesses should carefully review their insurance documents for specific exclusions or caps on these incidents.
Don’t skip the fine print! Many policies exclude nation-state attacks or limit coverage for unpatched vulnerabilities. Understanding these exclusions is critical.
Why Cyber Insurance Is Important
Cyber insurance is more than just a safety net; it protects financial stability, preserves business continuity, and manages liability. Here’s why it matters.
1. Financial Protection
The costs of cyber events can add up quickly. Expenses such as forensic investigations, legal fees, and downtime can easily exceed six or seven figures. For small and mid-sized businesses, this could spell disaster. Cyber insurance offers a vital financial cushion to absorb these costs.
2. Liability Management
Data breaches can lead to class-action lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage. Cyber insurance helps manage liabilities arising from legal claims and regulatory penalties.
Example: If customer data is stolen in a breach, your insurance policy can cover settlement payouts and defense costs.
3. Business Continuity
Recovering quickly from a breach is essential. Cyber insurance provides resources for expedited incident response, helping to minimize revenue loss and restore customer trust faster.
Learn more about how Balbix helped reduce Carvana’s cyber insurance premiums.
Who Needs Cyber Insurance?
The short answer? Anyone connected to the digital world. However, certain profiles can benefit most from cyber insurance, including:
- Mid-market or enterprise companies manage large amounts of customer data.
- Highly regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and education have strict compliance requirements.
- Technology-dependent businesses rely on the cloud or remote workforces.
- Organizations with limited incident response capabilities or immature cybersecurity programs.
Cyber insurance is a smart investment if a cybersecurity event could disrupt operations or affect your bottom line.
Cyber Insurance Complements, Not Replaces, Security
You can’t rely on cyber insurance to keep you safe. Think of it as an essential piece of a bigger puzzle. Alongside securing your digital infrastructure and cultivating strong security protocols, insurance helps mitigate risks when prevention fails.
Key takeaway: Cyber insurance won’t stop attacks, but it ensures financial recovery, operational stability, and preserved trust after they occur.
With the threat landscape continually evolving, it’s crucial to regularly assess your coverage for exclusions, limits, and adequacy based on your organization’s risk profile.
Want to learn more about building a cyber risk strategy? Read our guide on Understanding Cyber Risk Posture or explore how Balbix can effectively reduce your risk and quantify costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between first-party and third-party cyber insurance coverage?
-
First-party coverage handles losses directly impacting your business, such as data recovery and interruption. Conversely, third-party coverage protects you from legal and compliance fallout, including legal defense and regulatory fines.
- Does cyber insurance cover ransomware attacks?
-
Many cyber insurance policies cover ransomware attacks, including ransom payments, forensic investigations, and system restoration costs. However, reviewing your policy is essential, as some may have exclusions or limits.
- What types of businesses should consider cyber insurance?
-
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from cyber insurance, especially those handling sensitive customer data or operating in highly regulated industries such as healthcare, finance, and education. Companies with limited cybersecurity resources or those reliant on digital infrastructure should also consider it.
- Is cyber insurance a substitute for strong cybersecurity practices?
-
No, cyber insurance is not a replacement for robust cybersecurity measures. It complements security protocols by providing financial recovery and operational stability when preventive measures fail.
- Do all insurance policies cover cybercrime-related incidents?
-
Not all cyber insurance policies cover cybercrime incidents such as phishing, social engineering, and wire transfer fraud. It’s important to check your policy for specific exclusions or caps related to these risks.