Managing IT environments is no small feat. From countless assets like servers and applications to complex configurations and interdependencies, IT professionals are tasked with maintaining visibility and control. This is where a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) comes into play.
A CMDB is your IT infrastructure’s backbone, providing a centralized repository to track assets, their configurations, and relationships. Whether you’re dealing with routine system updates or responding to incidents, a well-maintained CMDB helps streamline IT operations.
Let’s explore a CMDB, what data it stores, how it works and why it is important.
What is a CMDB?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository that stores detailed information about the hardware, software, systems, and relationships that make up your IT environment.
Think of it as a core inventory that helps IT teams understand what they have, how it’s connected, and how changes will impact the broader system. CMDBs are often described as the “single source of truth” for IT assets and configurations. While that’s the goal, the reality is often more complex.
A CMDB contributes to a single source of truth in modern IT ecosystems, but it may not be the only one. Many organizations use a federated data model, where the CMDB aggregates and reconciles information from multiple sources—such as discovery tools, IT service management (ITSM) systems, cloud platforms, and security tools. This approach helps ensure more complete, current, and trustworthy data across dynamic environments.
Ultimately, a well-maintained CMDB supports smarter decision-making across IT operations, change management, incident response, and cybersecurity.
The Purpose of a CMDB
CMDBs help IT teams gain visibility and control over their technology landscape. They bridge the gap between IT assets and processes, allowing better management, troubleshooting, and planning.
A CMDB answers questions like:
- What assets are in my environment?
- How are these assets configured?
- What dependencies exist between them?
What Does a CMDB Store?
The information a CMDB captures is critical for understanding your IT systems’ structure, relationships, and operation. It provides a unified view of an organization’s IT assets and interdependencies, essential for informed decision-making.
Key Data Stored in a CMDB:
- Hardware Assets: A CMDB tracks all physical devices deployed across the organization, such as servers, desktops, laptops, routers, switches, printers, and other critical hardware components. It also includes details like serial numbers, warranty information, and physical locations of these devices.
- Software Information: The database stores information on applications, operating systems, licenses, and associated metadata. This includes versioning, license expiration dates, and patch levels, ensuring that software assets are properly managed and compliant with licensing agreements.
- Network Configurations: A CMDB includes details about network elements such as IP addresses, DNS configurations, firewalls, VLANs, and switches. By capturing this data, organizations can better manage network setups, troubleshoot connection issues, and maintain security configurations.
- Relationships and Dependencies: Understanding how different assets interact is one of the most valuable aspects of a CMDB. It maps relationships, such as which applications depend on specific hardware, which systems rely on shared databases, or how different network components are linked. This insight is crucial for assessing the impact of changes or outages across the IT environment.
This layered and highly detailed information enables the creation of a visual map of the entire IT ecosystem. With this map, teams can quickly identify root causes during troubleshooting, plan upgrades and new deployments effectively, and conduct a thorough risk analysis to avoid potential disruptions.
Why is a CMDB Important?
Implementing a CMDB is not just about cataloging IT assets; it’s a strategic move to optimize IT operations and drive business value.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: A CMDB reduces manual work by centralizing asset information. IT teams no longer waste time digging through disparate systems to find critical data.
- Streamlined Troubleshooting: When issues arise, visualizing dependencies in the CMDB helps identify root causes faster by pinpointing which assets are affected.
- Risk-Free Change Management: CMDBs assess the impact of planned changes, ensuring updates don’t inadvertently disrupt interconnected systems.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: For regulated industries, tracking configuration changes and maintaining an audit trail simplifies meeting compliance requirements.
How Does a CMDB Work?
Maintaining a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) involves a series of critical processes designed to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and usability of the data it contains.
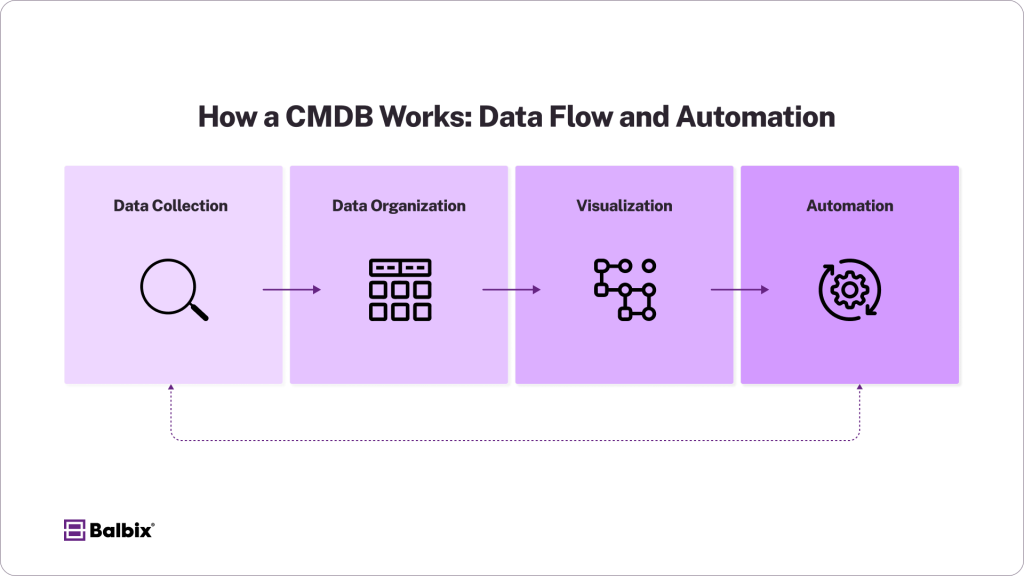
Let’s discuss the four key processes of how a CMDB works:
Key Processes of a CMDB:
Data Collection
The process starts with gathering information about IT assets, configurations, and relationships using automated discovery tools. These tools can scan networks to find devices, applications, and services, collecting details such as serial numbers, hardware specifications, installed software versions, IP addresses, and network locations. This data forms the foundation of the CMDB, helping IT teams understand the current state of their IT environment.
Data Organization
Once data is collected, it needs to be structured and categorized for easy access and usability. The CMDB organizes this information into predefined classes, such as hardware, software, or networking equipment. For example, servers might be grouped under a “hardware” class, while applications are categorized under a “software” class. This classification makes it easier to manage large volumes of data and quickly retrieve relevant information when needed.
Visualization
Modern CMDBs include powerful visualization tools representing dependencies, relationships, and service maps. These visualizations help IT teams understand how various elements are connected, making it easier to identify potential risks, troubleshoot issues, or assess the impact of planned changes.
For instance, a service map might reveal how a critical application depends on specific servers or network components, offering a clear picture of how disruptions could affect the system.
Automation
CMDBs increasingly rely on automation to maintain accuracy and reduce the burden of manual updates. Automated processes ensure asset details, such as configuration changes or new deployments, are updated in real-time. This minimizes the risk of human error and ensures the CMDB reflects the current state of the IT environment.
For example, if a server’s software is updated, the CMDB automatically reflects the change, keeping the data accurate and reliable.
These processes work together to ensure a CMDB remains up-to-date, comprehensive, and reliable.
Examples of Popular CMDBs
Not all CMDBs are created equal. The right tool depends on your organization’s size, complexity, and specific needs. Here are some popular options.
- ServiceNow CMDB: ServiceNow offers robust integration capabilities, making it an excellent choice for large enterprises seeking seamless workflows.
- BMC Helix CMDB: Designed for dynamic environments, BMC Helix provides advanced change management features to adapt to ongoing operational shifts.
- SolarWinds Service Desk: Ideal for small to medium businesses, this solution integrates IT service management with a simple and intuitive CMDB.
- Open Source Options like i-doit: i-doit is a budget-friendly, open-source alternative for organizations looking to avoid licensing costs while maintaining robust functionality.
When choosing a CMDB, consider factors like budget, existing tool compatibility, and required scalability.
Supercharge Your IT Operations
CMDBs provide the visibility, control, and efficiency necessary for modern IT management. Whether troubleshooting incidents, managing change, or preparing for audits, a CMDB ensures your IT operations run smoothly.
Are you curious about how integrating Balbix with your CMDB can further enhance your workflows? Learn more about Balbix today and see how we simplify IT asset management and cyber risk reduction.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a CMDB?
-
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository that stores information about IT assets and their relationships, helping organizations manage infrastructure efficiently.
- Which organizations benefit the most from a CMDB?
-
CMDBs benefit businesses with complex IT environments, especially those in regulated industries or those managing large asset inventories.
- How does a CMDB improve cyber risk management?
-
A CMDB identifies vulnerabilities, assesses potential risks, and enhances proactive security measures by mapping IT dependencies and tracking configurations.
- Can a CMDB integrate with other IT tools?
-
Yes, leading CMDBs integrate with ITSM platforms, network monitoring systems, and security tools to create a unified, automated IT ecosystem.
- Is maintaining a CMDB resource-intensive?
-
While initial setup requires effort, modern CMDBs leverage automation to streamline data updates and minimize ongoing maintenance.