You’re not alone if your organization is still running end-of-life (EOL) software. Many companies cling to outdated software due to cost, operational dependency, or simple oversight. However, unsupported software doesn’t just slow down your business—it opens the door to significant cyber risks.
This article explores the hidden risks, financial impacts, and compliance challenges of using EOL software and offers actionable strategies for mitigating these issues effectively.
What Is End-of-Life (EOL) Software?
EOL software refers to software no longer actively supported by the vendor, meaning it doesn’t receive updates, bug fixes, or security patches. Without these critical updates, vulnerabilities are left unaddressed, creating easy targets for cyberattacks.
Examples of EOL Software:
- Operating Systems: Windows 7, Windows Server 2012, macOS High Sierra.
- Enterprise Applications: Older versions of SAP, Oracle, and Adobe Flash.
- Networking Equipment: Legacy Cisco IOS, outdated firewalls, routers.
- Custom Software: Internally developed tools with no active maintenance.
Using EOL software isn’t just risky; it undermines your organization’s cyber risk posture.
Top EOL Software Risks
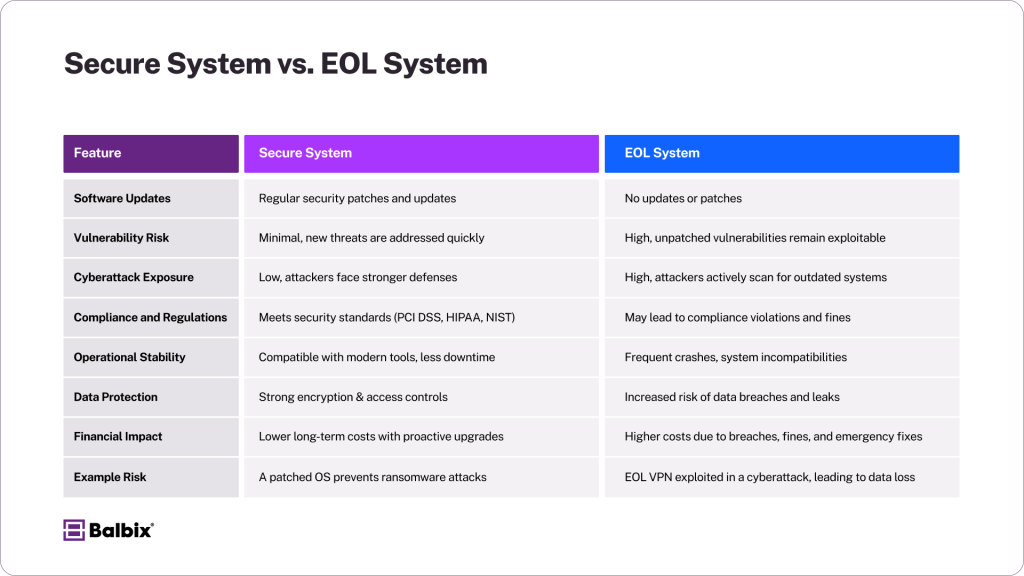
Consider the comparison image below of a secure system versus an end-of-life system. Let’s discuss the risks in depth and mitigation strategies:
Increased Attack Surface & Exploitable Vulnerabilities
- No Security Patches: Once software reaches its end of life (EOL), vendors stop releasing updates and patches, exposing vulnerabilities to new and evolving threats. Without these patches, attackers can exploit minor bugs to gain unauthorized access or disrupt systems.
- Prime Targets for Cybercriminals: Cybercriminals actively monitor organizations that are still using EOL software, as it provides an easy entry point. Attackers use automated tools to scan for outdated systems, exploiting vulnerabilities that have long been documented but remain unaddressed due to the lack of updates.
Real-World Warning:
In 2023, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued an alert regarding the active exploitation of EOL SonicWall VPNs. Despite the known risks, thousands of organizations continued using these outdated systems, leaving themselves vulnerable to attacks that could have been prevented with updated software.
Compliance & Regulatory Risks
Running EOL software risks your systems and can lead to serious legal and compliance issues. Many regulatory frameworks across industries mandate using updated, secure systems to protect sensitive data and ensure operational integrity.
Key Compliance Pitfalls:
- PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requires organizations that process payments to use secure, supported software. Failure to comply can result in steep fines, suspension of payment processing capabilities, and reputational harm.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) demands robust protections for patient healthcare data. EOL software that lacks these protections puts organizations at risk of data breaches and massive penalties.
- NIST & CISA Directives: Both organizations actively discourage the use of EOL systems, particularly in critical infrastructure and government-related environments, as they are considered high-risk vulnerabilities.
Example:
If a data breach occurs, a healthcare organization relying on outdated EOL software to manage patient records could face severe penalties. Beyond financial losses, such an incident could lead to compromised patient trust and long-term reputational damage.
In addition, auditors can flag EOL systems during compliance reviews, resulting in costly fines, mandatory upgrades, or even the loss of certifications necessary to operate within specific industries.
Operational Costs & Productivity Loss
While EOL software might seem like a cost-effective choice in the short term, it often leads to hidden costs that escalate over time, severely straining operational budgets and resources.
- Higher Maintenance Costs: IT teams must create custom patches to address security vulnerabilities without vendor support, which is time-consuming and expensive. Alternatively, organizations may opt for costly extended support from vendors, which can quickly add up.
- Compatibility Issues: EOL software often struggles to integrate with modern tools, cloud platforms, and workflows. This can lead to delays, inefficiencies, and frustration among employees who depend on these systems to perform daily tasks.
- System Failures: Using outdated software on unsupported hardware increases the risk of crashes, downtime, and data loss. These failures can disrupt operations, impact customer experience, and result in significant financial losses.
Example:
A manufacturing company experienced a week-long production halt when its EOL software failed to integrate with a new cloud-based inventory management system. The downtime cost the company millions in lost revenue and delayed shipments, highlighting the risks of relying on outdated tools.
Beyond direct costs, the productivity loss from slow, outdated systems can frustrate employees and hinder overall business growth.
Third-Party & Supply Chain Risks
Even if your organization maintains up-to-date software, third-party vendors or partners using EOL systems can still compromise your security posture. These weaknesses in the supply chain often manifest via compromised libraries (log4j is a recent example) and provide attackers with an indirect but effective entry point into your systems.
Read more about software supply chain vulnerabilities and how to secure them.
Example:
A major healthcare provider suffered a significant data breach in 2018, which was traced back to an unpatched EOL Citrix server used by one of its third-party vendors—the breach exposed sensitive patient data, leading to costly lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage.
Supply chain vulnerabilities are becoming increasingly common as organizations rely on a network of external partners and vendors to deliver their services. Attackers often exploit the weakest link in the chain, making it critical for organizations to ensure that third parties adhere to the same security standards, including avoiding using EOL software.
Tip:
Conduct regular security audits of your vendors and partners to ensure they are not running EOL systems. Include contract clauses requiring them to maintain up-to-date software and follow best security practices.
Strategies for Mitigating EOL Software Risks
1. Improve Asset Visibility
You can provide better protection if you know what you’re protecting. The first step is to gain complete visibility into your environment by implementing automated asset inventory tools that consolidate the key inventory sources. These tools can help identify all End-of-Life (EOL) software instances across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. A thorough inventory provides a foundation for understanding the scope of your EOL risks and effectively planning remediation efforts.
Tip:
Remember to monitor for transient systems, shadow IT, and IOT/OT devices, as these often harbor EOL assets and OSs that may escape detection by traditional inventory tools. Regular scans and audits can help ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
2. Prioritize Risks Based on Impact
Not all EOL software poses the same level of risk, so it’s essential to prioritize based on the potential impact on your business. Evaluate how critical each system is to your operations and the likelihood of being targeted or exploited. Based on this assessment, apply a phased approach to remediation:
- Replace or upgrade critical systems: Start with software integral to your business processes or poses a high-security risk.
- Use extended vendor support selectively: When immediate upgrades are impossible, consider using extended support programs.
- Implement compensating controls: To mitigate risks for systems that cannot be replaced immediately, deploy controls such as additional monitoring and access restrictions.
- Track all exceptions and compensating controls: Most compliance and security frameworks mandate time restrictions on exceptions and compensating controls, so ensure you have a process or a tool that can track all of the accepted risk instances.
By first addressing the most critical risks, you can balance operational needs with your security strategy while working toward a complete resolution.
3. Enforce Secure Configurations
For EOL systems that cannot be retired immediately, take steps to minimize risk exposure by enforcing secure configurations, including:
- Restrict External Access: To contain potential vulnerabilities, isolate outdated software from the broader network. Place these systems behind firewalls or in isolated VLANs to limit exposure.
- Harden Configurations: Disable unnecessary services, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enable advanced logging to monitor activity and detect suspicious behavior.
- Microsegmentation: Use microsegmentation techniques to create strict boundaries between EOL systems and sensitive environments, reducing the potential for lateral movement in the event of a breach.
These measures significantly reduce the attack surface and provide an added layer of security while you transition to supported systems. Implementing adherence to a prescriptive best-practice secure configuration community like the benchmarks from the Center for Internet Security (CIS) can jump-start this process.
4. Enable Virtual Patching
Virtual patching can be an alternative safeguard against vulnerabilities when official vendor patches are no longer available. Tools like web application firewalls (WAFs), advanced endpoint protection, and intrusion prevention systems can help shield EOL systems from known exploits.
Additionally, consider these proactive steps:
- Regularly review vendor support timelines to anticipate and mitigate future EOL risks before they become critical.
- Automate patching processes for supported systems to address vulnerabilities as soon as updates are released, ensuring new risks don’t pile up while you focus on older systems.
Taking a proactive and layered approach to managing EOL software risks protects your organization’s security posture and helps maintain operational resilience and compliance with industry standards.
How Balbix Can Help Reduce EOL Software Risk
Enterprise environments are complex, and manually tracking EOL software is nearly impossible. Balbix simplifies this process with AI-driven solutions designed for security leaders like you.
- Automated Asset Discovery: Continuously scans your IT ecosystem to detect EOL software.
- Risk Quantification: Prioritizes high-risk EOL assets based on business impact and threat likelihood.
- AI-Powered Remediation Insights: Provides actionable steps—upgrade, patch, isolate, or replace—tailored to your specific environment.
- Continuous Monitoring: Flags newly discovered EOL software before it becomes a critical vulnerability.
- Risk acceptance workflow: Enhances visibility to exceptions and compensating controls to reduce audit findings due to missed patch windows
Proactive Management for a Stronger Cyber Risk Posture
End-of-life software is more than a security risk—it’s a liability that impacts compliance, operations, and finances. The hidden costs of running outdated systems often outweigh the perceived benefits of “keeping them for just a little longer.”
By proactively identifying and addressing EOL software, your organization can reduce its attack surface, improve compliance posture, and safeguard critical assets.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is running end-of-life software a security risk?
-
End-of-life (EOL) software is a major security risk because it no longer receives vendor patches, bug fixes, or security updates. This exposes known vulnerabilities, making it an easy target for cybercriminals who exploit outdated systems to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or disrupt operations.
- How does EOL software impact compliance with cybersecurity regulations?
-
Many regulations, including PCI DSS, HIPAA, and NIST guidelines, require organizations to maintain up-to-date, secure software. Using EOL software can lead to compliance violations, fines, and even legal action, increasing the risk of data breaches and weakening overall cybersecurity defenses.
- What are the hidden costs of keeping outdated software?
-
While avoiding upgrades might seem cost-effective, maintaining EOL software often results in hidden costs such as:
- Expensive extended vendor support
- Custom security patches from IT teams
- Increased downtime and productivity losses due to compatibility issues
- Higher cybersecurity insurance premiums due to increased risk exposure
- Can virtual patching protect EOL software from cyber threats?
-
Virtual patching can help mitigate some risks by blocking known exploits using firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and endpoint protection. However, it’s not a long-term solution, as new vulnerabilities will continue to emerge, and these systems cannot fully replace vendor security updates.
- What’s the best strategy for managing end-of-life software risks?
-
The best approach combines proactive asset discovery, risk prioritization, and phased upgrades. Organizations should:
- Identify all EOL software using automated asset inventory tools
- Prioritize replacement based on business impact and security risk
- Implement compensating controls, such as network segmentation and restricted access, for software that can’t be replaced immediately
- Plan future upgrades to avoid last-minute compliance and security issues